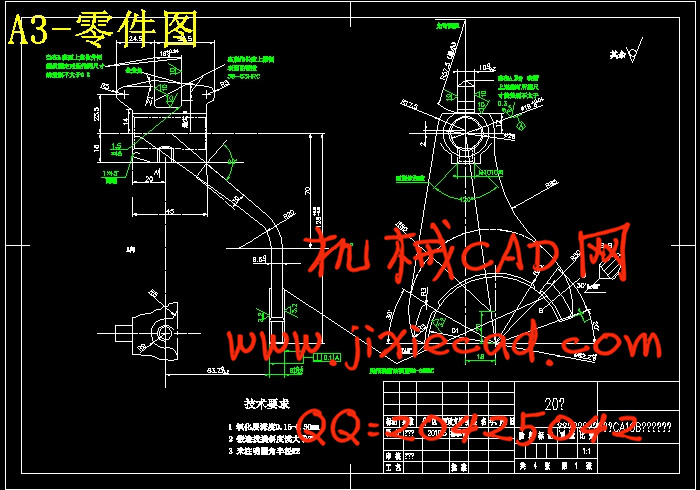
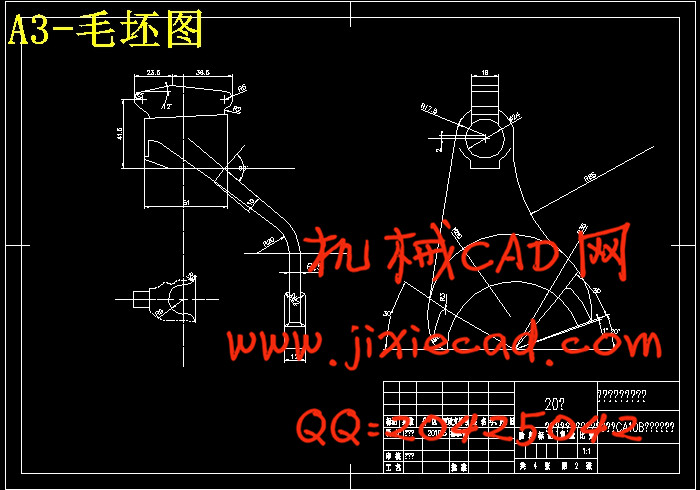
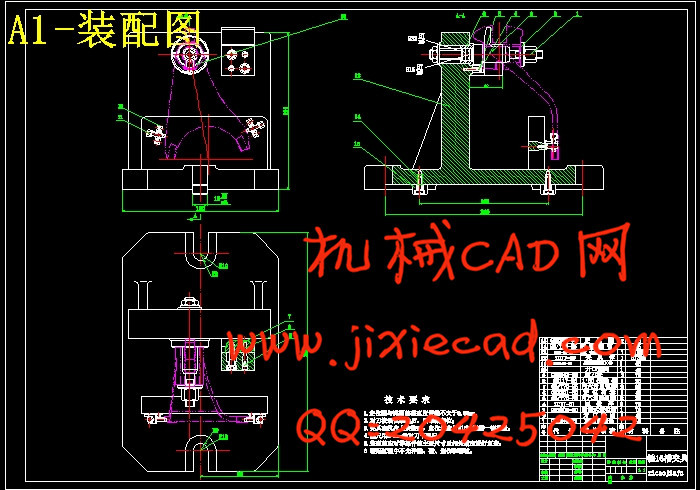
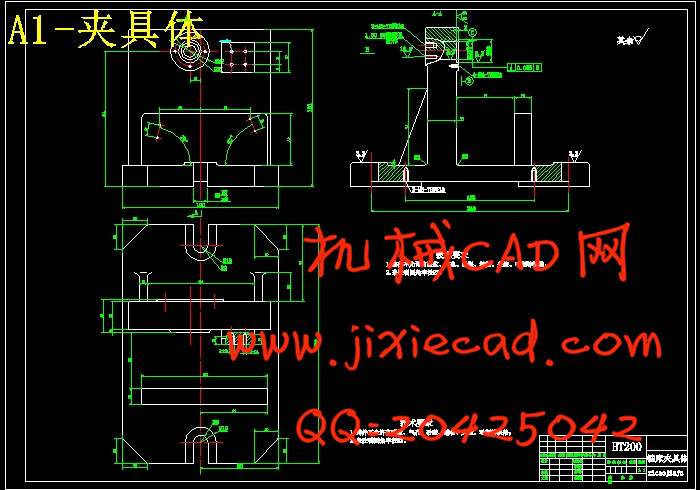
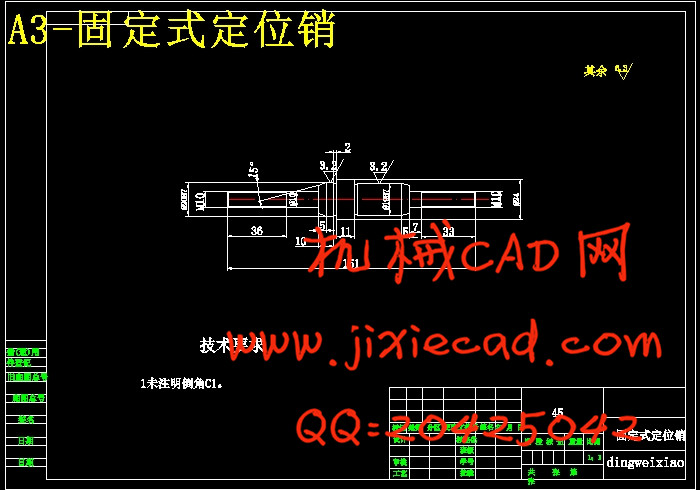
设计简介
摘 要
本设计是基于汽车拨叉零件的加工工艺规程及一些工序的专用夹具设计。汽车拨叉零件的主要加工表面是平面及孔系。一般来说,保证平面的加工精度要比保证孔系的加工精度容易。因此,本设计遵循先面后孔的原则。并将孔与平面的加工明确划分成粗加工和精加工阶段以保证孔系加工精度。主要加工工序安排是先以支承孔系定位加工出顶平面,再以顶平面与支承孔系定位加工出工艺孔。在后续工序中除个别工序外均用顶平面和工艺孔定位加工其他孔系与平面。支承孔系的加工采用的是坐标法镗孔。整个加工过程均选用通用。夹具选用专用夹具,夹紧方式多选用气动夹紧,夹紧可靠,机构可以不必自锁,因此生产效率较高,适用于大批量、流水线上加工,能够满足设计要求。
关键词:汽车拨叉零件;工艺;夹具;
ABSTRACT
This design is the special fixture for machining technology for the chemical pipeline parts and process design based on. The main processing surface chemical pipeline parts is the plane and a series of hole. In general, ensure the machining accuracy of plane than to ensure the accuracy of the processing easily. Therefore, the design follows the surface after the first hole principle. And the hole and the plane processing clearly divided into roughing and finishing stages to ensure machining precision. The main process of machining technology is first to support hole positioning processing the top plane, and then the top plane and the series of supporting hole location hole processing technology. In addition to the follow-up processes are individual processes with the top plane positioning technology and other processing Kong and plane. Processing support holes using the coordinate boring. The whole process selection of general. The special fixture fixture, clamping means more choice of pneumatic clamping, clamping reliable, agencies can not self-locking, therefore the production efficiency is high, suitable for large batch, line processing, can meet the design requirements.
Keywords: chemical pipe parts; technology; fixture;
目 录
摘 要·································································································· II
ABSTRACT······························································································· III
第一章 机械加工工艺规程设计········································································ 2
1.1 零件的分析····················································································································································· 2
1.1.1 零件的作用········································································································· 2
1.2 汽车拨叉加工的主要问题和工艺过程设计所应采取的相应措施·············································· 3
1.2.1 孔和平面的加工顺序··························································································· 3
1.2.2 孔系加工方案选择······························································································· 3
1.3 汽车拨叉加工定位基准的选择··············································································································· 4
1.3.1 粗基准的选择······································································································ 4
1.3.2 精基准的选择······································································································ 4
1.4 汽车拨叉加工主要工序安排···················································································································· 4
1.5 机械加工余量、工序尺寸及毛坯尺寸的确定··················································································· 6
1.6 毛坯种类的选择··········································································································································· 7
1.7 选择加工设备和工艺装备························································································································· 8
1.7.1 机床选用············································································································ 8
1.7.2 选择刀具············································································································ 8
1.7.3 选择量具············································································································ 8
1.8 机械加工余量、工序尺寸及毛坯尺寸的确定··················································································· 8
1.9确定切削用量及基本工时(机动时间)···························································································· 10
1.10 时间定额计算及生产安排···················································································································· 21
第2章 铣16槽夹具的设计··········································································· 23
2.1 问题的提出··········································································································· 23
2.2 夹具设计··············································································································· 23
2.2.1 定位基准的选择·································································································· 23
2.2.2切削力和夹紧力计算····························································································· 23
2.2.3定位误差分析······································································································ 25
2.2.4夹具设计及操作的简要说明··················································································· 26
总 结·········································································································· 27
参考文献····································································································· 28
致 谢··································································································· 29
本设计是基于汽车拨叉零件的加工工艺规程及一些工序的专用夹具设计。汽车拨叉零件的主要加工表面是平面及孔系。一般来说,保证平面的加工精度要比保证孔系的加工精度容易。因此,本设计遵循先面后孔的原则。并将孔与平面的加工明确划分成粗加工和精加工阶段以保证孔系加工精度。主要加工工序安排是先以支承孔系定位加工出顶平面,再以顶平面与支承孔系定位加工出工艺孔。在后续工序中除个别工序外均用顶平面和工艺孔定位加工其他孔系与平面。支承孔系的加工采用的是坐标法镗孔。整个加工过程均选用通用。夹具选用专用夹具,夹紧方式多选用气动夹紧,夹紧可靠,机构可以不必自锁,因此生产效率较高,适用于大批量、流水线上加工,能够满足设计要求。
关键词:汽车拨叉零件;工艺;夹具;
ABSTRACT
This design is the special fixture for machining technology for the chemical pipeline parts and process design based on. The main processing surface chemical pipeline parts is the plane and a series of hole. In general, ensure the machining accuracy of plane than to ensure the accuracy of the processing easily. Therefore, the design follows the surface after the first hole principle. And the hole and the plane processing clearly divided into roughing and finishing stages to ensure machining precision. The main process of machining technology is first to support hole positioning processing the top plane, and then the top plane and the series of supporting hole location hole processing technology. In addition to the follow-up processes are individual processes with the top plane positioning technology and other processing Kong and plane. Processing support holes using the coordinate boring. The whole process selection of general. The special fixture fixture, clamping means more choice of pneumatic clamping, clamping reliable, agencies can not self-locking, therefore the production efficiency is high, suitable for large batch, line processing, can meet the design requirements.
Keywords: chemical pipe parts; technology; fixture;
目 录
摘 要·································································································· II
ABSTRACT······························································································· III
第一章 机械加工工艺规程设计········································································ 2
1.1 零件的分析····················································································································································· 2
1.1.1 零件的作用········································································································· 2
1.2 汽车拨叉加工的主要问题和工艺过程设计所应采取的相应措施·············································· 3
1.2.1 孔和平面的加工顺序··························································································· 3
1.2.2 孔系加工方案选择······························································································· 3
1.3 汽车拨叉加工定位基准的选择··············································································································· 4
1.3.1 粗基准的选择······································································································ 4
1.3.2 精基准的选择······································································································ 4
1.4 汽车拨叉加工主要工序安排···················································································································· 4
1.5 机械加工余量、工序尺寸及毛坯尺寸的确定··················································································· 6
1.6 毛坯种类的选择··········································································································································· 7
1.7 选择加工设备和工艺装备························································································································· 8
1.7.1 机床选用············································································································ 8
1.7.2 选择刀具············································································································ 8
1.7.3 选择量具············································································································ 8
1.8 机械加工余量、工序尺寸及毛坯尺寸的确定··················································································· 8
1.9确定切削用量及基本工时(机动时间)···························································································· 10
1.10 时间定额计算及生产安排···················································································································· 21
第2章 铣16槽夹具的设计··········································································· 23
2.1 问题的提出··········································································································· 23
2.2 夹具设计··············································································································· 23
2.2.1 定位基准的选择·································································································· 23
2.2.2切削力和夹紧力计算····························································································· 23
2.2.3定位误差分析······································································································ 25
2.2.4夹具设计及操作的简要说明··················································································· 26
总 结·········································································································· 27
参考文献····································································································· 28
致 谢··································································································· 29