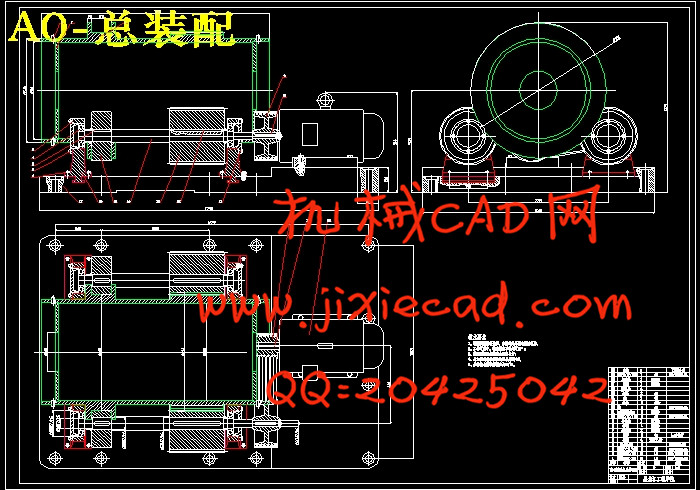
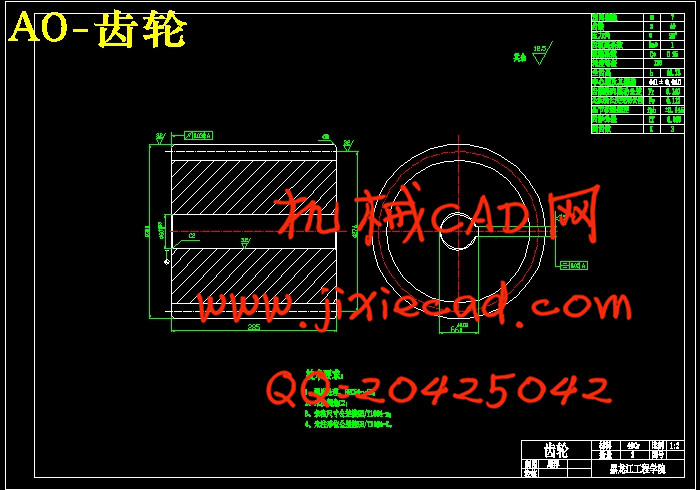
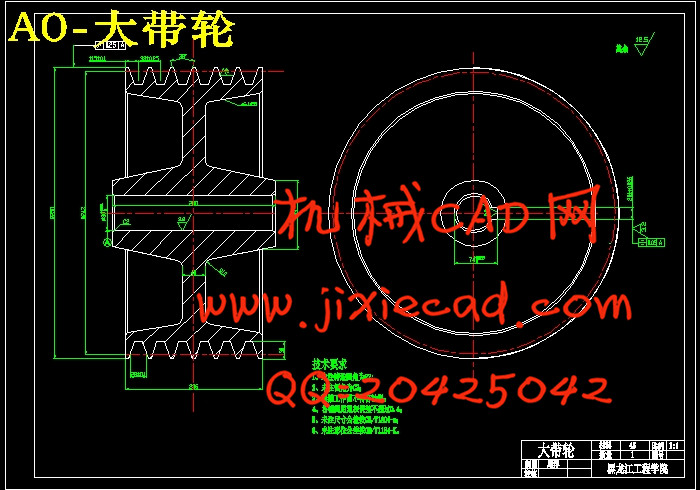
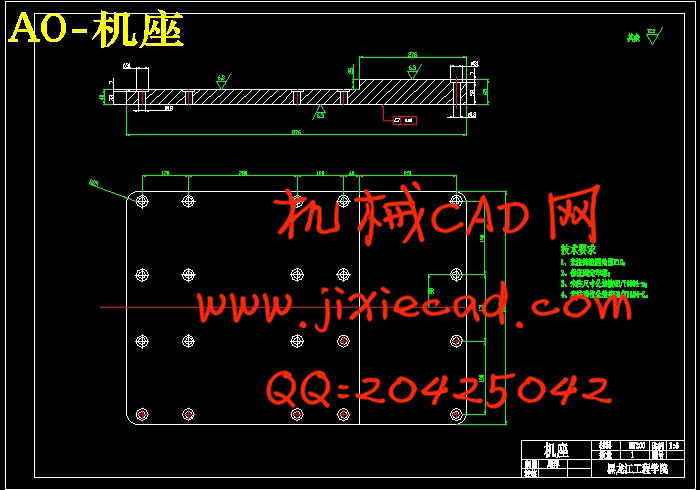
设计简介
摘 要
铸造是一种液态金属成型的方法。铸件已广泛应用于各工业部门和日常生活中,其中通过离心铸造而成的铸件占相当大的比重,离心铸造是将金属液浇入旋转的铸型中,在离心力作用下填充铸型而凝固成形的一种铸造方法,离心铸造是在离心机上进行的。离心铸造分为立式和卧式两种,卧式滚轮式离心铸造机包括:铸型,浇注系统,传动系统,以及电器控制系统几个部分。其工作过程包括:涂料,浇注,冷却,拔模,本设计利用现有的一些新元件对铸造机进行优化设计,并采用PLC进行控制,使之操作方便,结构简化,性能提升。本设计为滚筒式离心铸造机,加工直径 ,厚度在
,厚度在 到
到 之间的铜合金管型材料。
之间的铜合金管型材料。
关键词:铸造;浇注系统;离心铸造机;电器控制系统;滚筒式
ABSTRACT
Casting is a way to take shape of mentel liquide. In all kinds of industrial departments and every day life, casts are used widely. Especially the cast which made by centrifugal technology.centrifugal casting is a way that you should pour the mentel liquide into a revolving model, then by the power of centrifugal force fill up model till that solidify. It performances on centrifugal casting machine. There are two ways,one is vertical and the other is horizontal.
The horizontal contains the model,pour system,transimission system,and electronic control system.Its process is:pain,cool and take the model out.
This design takes use of exsited elements and controlled by PLC which operates more easily,simply but natural capacity is better.
Keywords:casting;pour system;centrifugal casting machine;electronic control system;Drum type
铸造是一种液态金属成型的方法。铸件已广泛应用于各工业部门和日常生活中,其中通过离心铸造而成的铸件占相当大的比重,离心铸造是将金属液浇入旋转的铸型中,在离心力作用下填充铸型而凝固成形的一种铸造方法,离心铸造是在离心机上进行的。离心铸造分为立式和卧式两种,卧式滚轮式离心铸造机包括:铸型,浇注系统,传动系统,以及电器控制系统几个部分。其工作过程包括:涂料,浇注,冷却,拔模,本设计利用现有的一些新元件对铸造机进行优化设计,并采用PLC进行控制,使之操作方便,结构简化,性能提升。本设计为滚筒式离心铸造机,加工直径
关键词:铸造;浇注系统;离心铸造机;电器控制系统;滚筒式
ABSTRACT
Casting is a way to take shape of mentel liquide. In all kinds of industrial departments and every day life, casts are used widely. Especially the cast which made by centrifugal technology.centrifugal casting is a way that you should pour the mentel liquide into a revolving model, then by the power of centrifugal force fill up model till that solidify. It performances on centrifugal casting machine. There are two ways,one is vertical and the other is horizontal.
The horizontal contains the model,pour system,transimission system,and electronic control system.Its process is:pain,cool and take the model out.
This design takes use of exsited elements and controlled by PLC which operates more easily,simply but natural capacity is better.
Keywords:casting;pour system;centrifugal casting machine;electronic control system;Drum type
目 录
摘要………………………………………………………………………………………Ⅰ
Abstract ………………………………………………………………………………Ⅱ
第1章 绪论……………………………………………………………………………1
1.1 概述……………………………………………………………………………1
1.2 离心铸造机的发展过程……………………………………………………2
1.3 离心铸造机的分类…………………………………………………………2
1.4 离心铸造特点…………………………………………………………………3
1.5 离心铸造基本原理……………………………………………………………4
1.6 离心铸造的发展前景…………………………………………………………4
1.7 本章小结………………………………………………………………………4
第2章 滚轮式离心铸造机的原理分析…………………………………5
2.1 离心力………………………………………………………………………5
2.2 离心力场……………………………………………………………………5
2.3 有效重度………………………………………………………………………5
2.4 自由表面………………………………………………………………………5
2.5 离心压力………………………………………………………………………7
2.6液体金属中异相质点的径向运动…………………………………………9
2.7 离心铸造的缩补…………………………………………………………10
2.8 离心铸件在液体金属相对影响下的凝固特点…………………………10
2.9 本章小结………………………………………………………………14
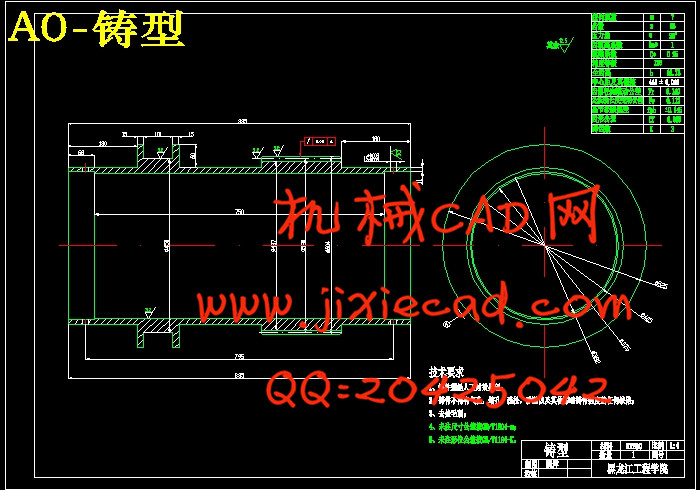
第3章 金属铸型的设计……………………………………………………15
3.1 卧式滚筒离心铸造机……………………………………………………15
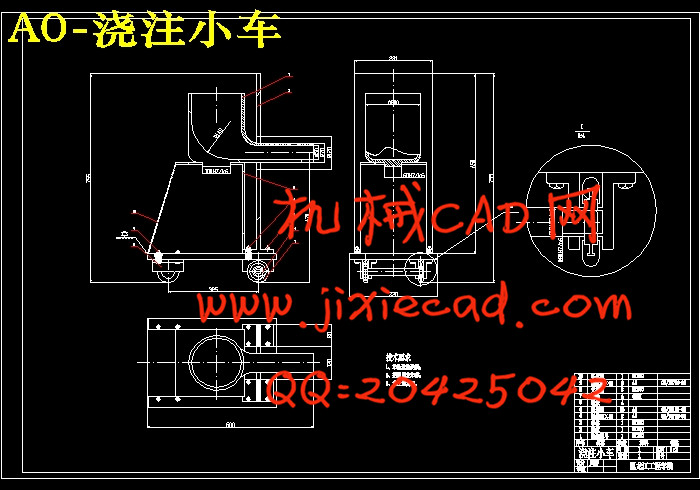
3.2 铸件类型选择………………………………………………………………15
3.3 铸型型体设计………………………………………………………………15
3.4铸型端盖和端盖紧固装置设计……………………………………………16
3.5滚筒式离心铸型的滚道和定位……………………………………………17
3.6 浇筑系统设计………………………………………………………………17
3.7 本章小结……………………………………………………………………18
第4章 电动机选择…………………………………………………………………19
4.1 铸型转速………………………………………………………………19
4.2 离心铸型壁厚………………………………………………………………19
4.3 离心压力……………………………………………………………………20
4.4 电动机功率选择…………………………………………………………20
4.5 本章小结…………………………………………………………………21
第5章 带传动的设计………………………………………………………22
5.1 V带的设计………………………………………………………………22
5.2 带轮结构的设计…………………………………………………………………23
5.3 本章小结……………………………………………………………………24
第6章 齿轮与带轮的设计…………………………………………………………25
6.1 齿轮的设计…………………………………………………………………25
6.2 齿面接触疲劳强度设计……………………………………………………25
6.3 第五、六齿轮设计………………………………………………………………26
6.4 校核齿轮齿根弯曲疲劳强度……………………………………………………26
6.5 将几何尺寸汇于表………………………………………………………………27
6.6 拖轮的设计………………………………………………………………………27
6.7 本章小结…………………………………………………………………………28
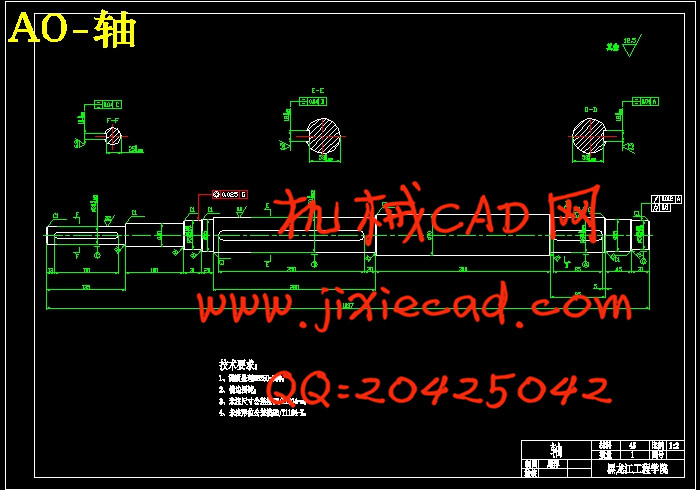
第7章 轴的设计及轴承与键的选择…………………………………………29
7.1 估算轴的基本直径………………………………………………………………29
7.2 轴的结构设计……………………………………………………………………29
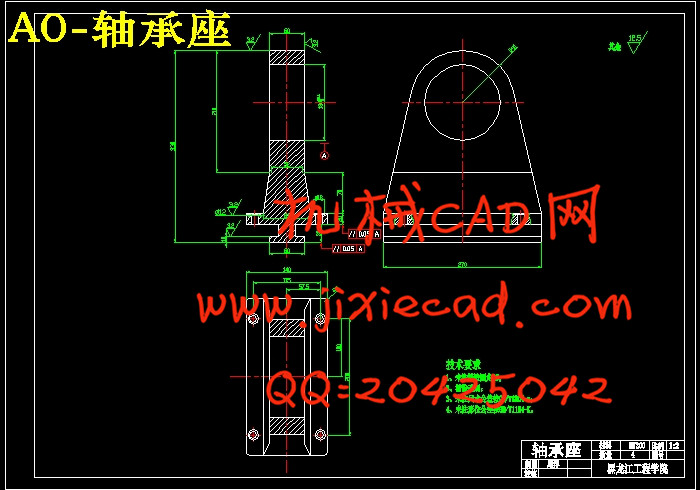
7.3 轴承的选择………………………………………………………………………29
7.4 键的选择…………………………………………………………………………29
7.5 轴的受力分析……………………………………………………………………30
7.5 本章小结…………………………………………………………………………32
结论………………………………………………………………………………………33
参考文献 ………………………………………………………………………………34
致谢………………………………………………………………………………………35