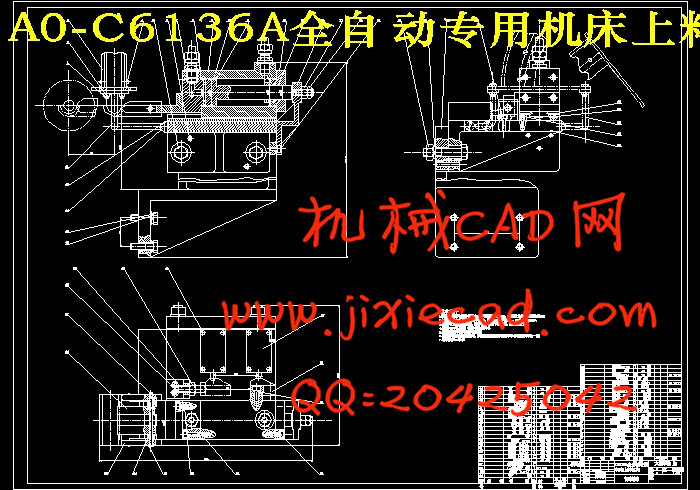
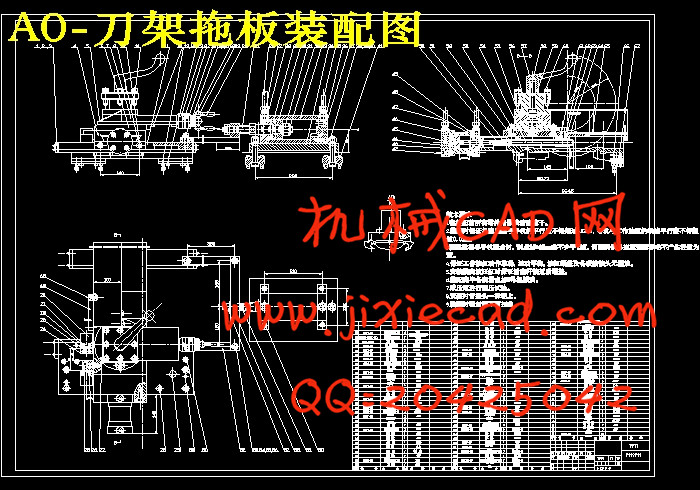
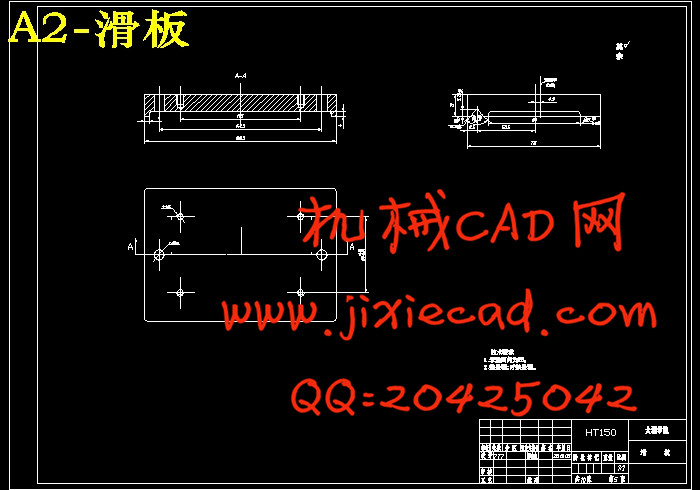
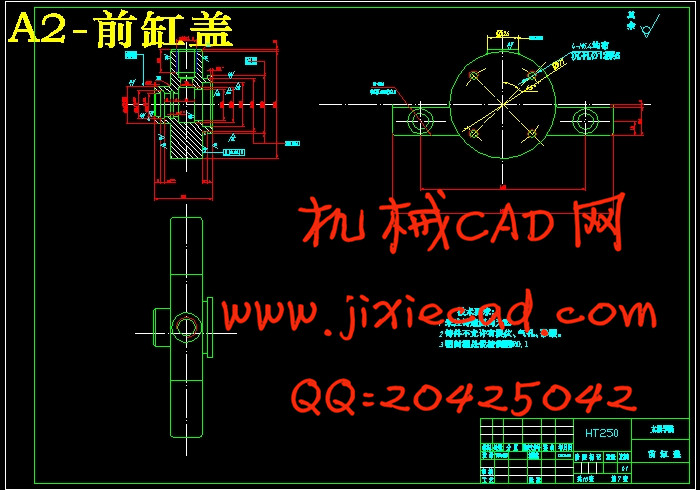
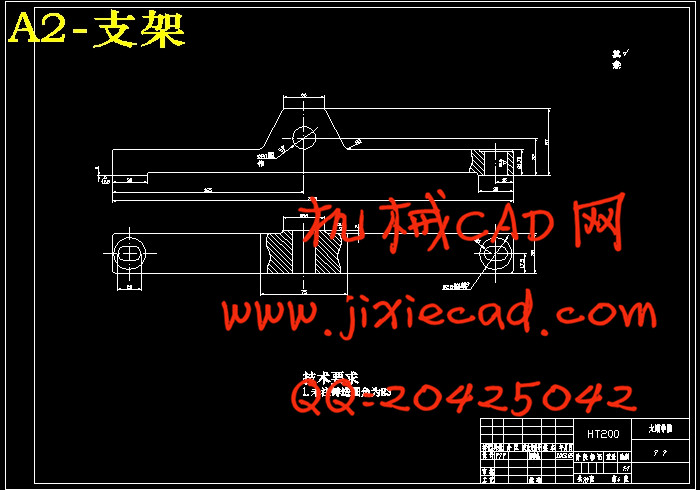
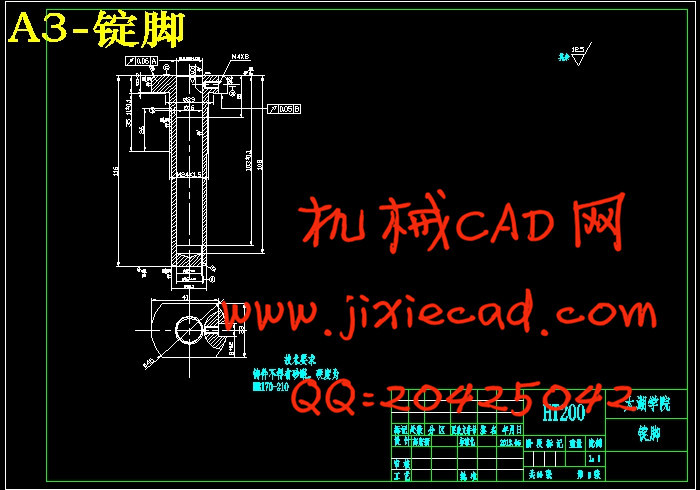
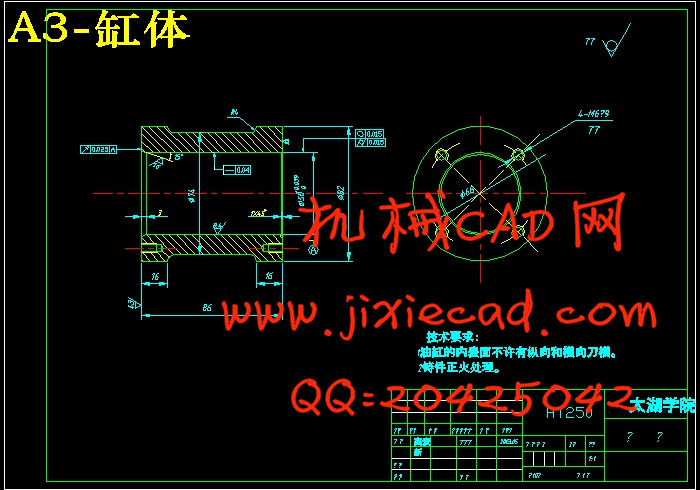
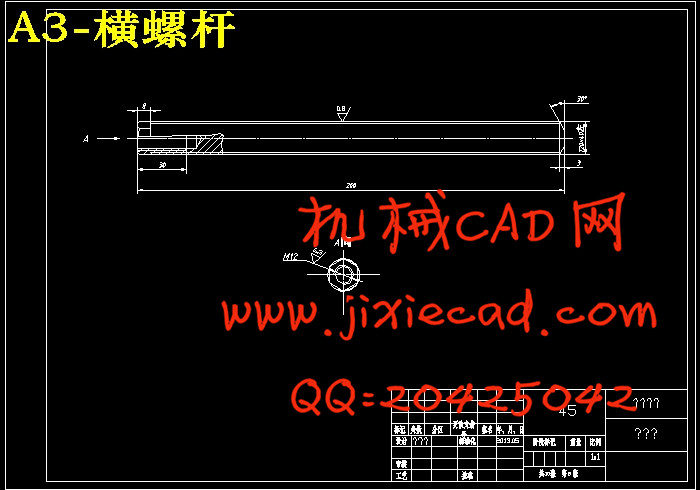
设计简介
摘 要
车床是主要用车刀对旋转的工件进行车削加工的机床,而专用机床一般采用多轴、多刀、多工序、多面或多工位同时加工的方式,生产效率比通用机床高几倍至几十倍。由于通用部件已经标准化和系列化,可根据需要灵活配置,能缩短设计和制造周期。因此专用机床兼有低成本和高效率的优点,在大批、大量生产中得到广泛应用,并可用以组成自动生产线。专用机床一般用于加工箱体类或特殊形状的零件。加工时,工件一般不旋转,由刀具的旋转运动和刀具与工件的相对进给运动,来实现钻孔、扩孔、锪孔、铰孔、镗孔、铣削平面、切削内外螺纹以及加工外圆和端面等。有的组合机床采用车削头夹持工件使之旋转,由刀具作进给运动,也可实现某些回转体类零件(如飞轮、汽车后桥半轴等)的外圆和端面加工。
本设计是把6136普通车床改造成全自动液压专用机床,对车床结构作了设计,在设计过程中考虑到车床的形成工艺,床身的受力分析和床身的热态分析。该设计满足了全自动液压专用机床的加工精度要求,整体性能稳定。
关键词:刀架拖板;液压缸;上料机构;分析
Abstract
Lathe is mainly used tool for rotating workpiece turning processing machine tools, and special machine tools commonly used multi-spindle, multi-tool, process, surface or transfer process at the same time, the production efficiency is higher than general machine tools several times or more. Due to gm parts have standardization and seriation, can be flexibly configured according to need, to shorten design and manufacturing cycle. So dedicated machine tool has both the advantages of low cost and high efficiency, is widely used in large, mass production, and can be used to form automatic production line.Dedicated box is generally used in the machine or special shaped parts. When the workpieces are generally not rotate, the by the rotation of the tool movement and relative feed movement of cutting tool and workpiece, to implement a drilling, reaming, counter boring, reaming, boring, milling plane, cylindrical internal and external screw thread and cutting processing and face, etc. Some combination machine tools using turning head clamping workpiece to rotate, the tool feed movement, also can achieve some of the revolving body parts, such as flywheel, vehicle driving axle half shaft, etc.) of the cylindrical and face processing.
This design is put 6136 ordinary lathe to transform into a special machine, automatic hydraulic structure design of the lathe, in the design process of forming process considering lathe bed, bed of the thermal stress analysis and modal analysis. The design of automatic hydraulic meet the special machine machining accuracy requirement, and overall stability.
Key words:Tool carriage apron;hydraulic cylinder;Feeding institutions;analysis
目 录
摘 要 IIIAbstract IV
目 录 V
1 绪论 1
2 零件的工艺性分析 2
3 总体方案的确定 4
4 刀架拖板设计 6
4.1 设计本部分的重要性 6
4.2 本部分的设计方案 6
4.2.1 纵向液压缸的安置 6
4.2.2 横向液压缸的位置 7
4.3 出屑 9
5 结构设计及计算分析 10
5.1 纵向液压缸的设计 10
5.1.1 液压缸的类型和安装形式 10
5.1.2 液压缸工作压力的确定 10
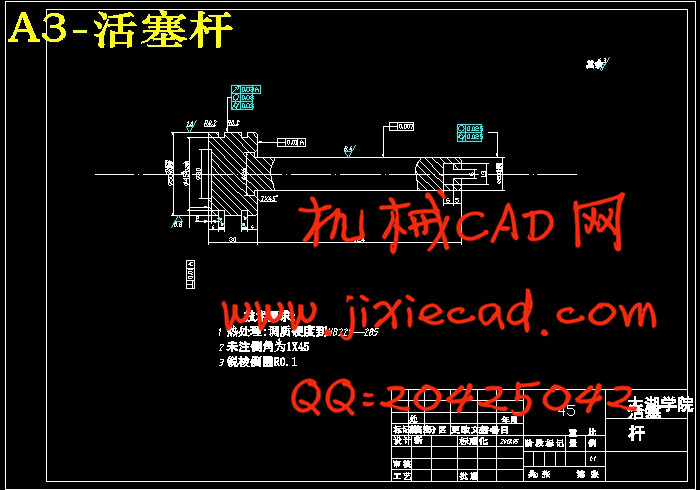
5.1.3 液压缸内径及液压缸活塞杆直径的确定 11
5.1.4 液压缸的推力和流量计算 12
5.1.5 活塞杆直径的验算 12
5.1.6 液压缸长度及壁厚的确定 13
5.1.7 液压缸外径的计算 13
5.1.8 液压缸进出油口尺寸的确定 13
5.1.9 液压缸的结构设计 13
5.2 横向液压缸的设计 14
5.2.1 液压缸的类型和安装形式 14
5.2.2 液压缸工作压力的确定 15
5.2.3 液压缸内径及液压缸活塞杆直径的确定 15
5.2.4 液压缸的推力和流量计算 15
5.2.5 活塞杆直径的验算 16
5.2.6 液压缸壁厚的计算和刹那高度的计算 16
5.2.7 压缸外径液的计算 16
5.2.8 液压缸进出油口尺寸的确定 16
5.2.9 液压缸的结构设计 17
5.3 弹簧的设计与计算 17
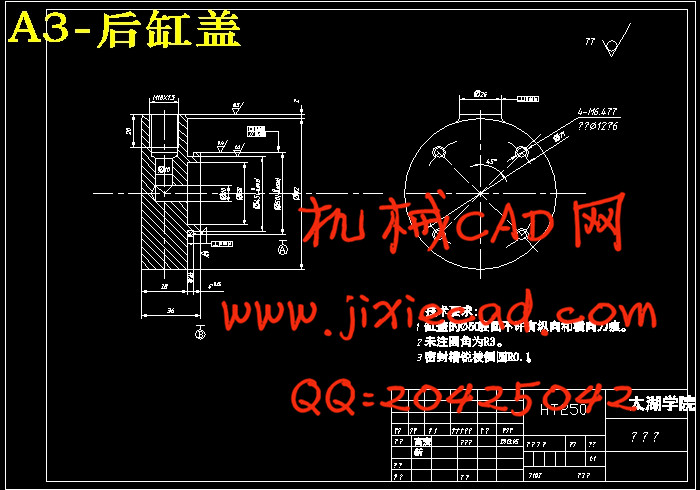
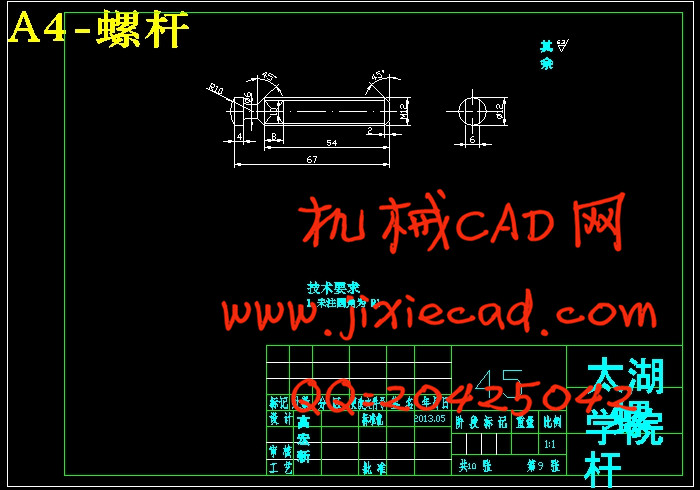
5.4 螺杆的校核 18
6 CAM设计 20
6.1 衬套的CAM 22
7 结论与展望 24
7.1 结论 24
7.2 展望 24
致 谢 25
参考文献 26