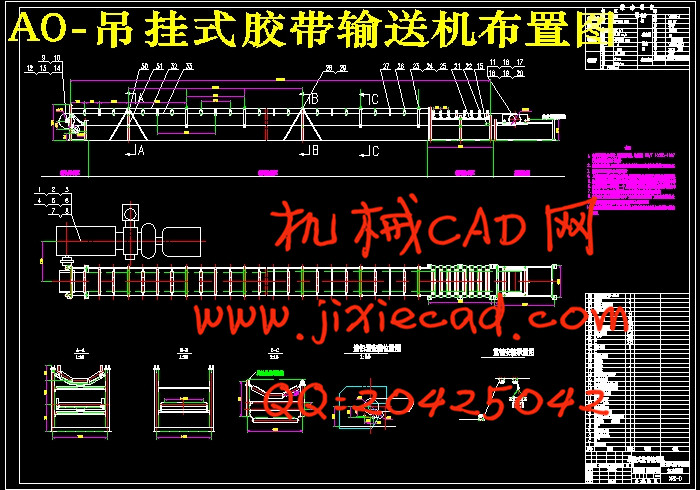
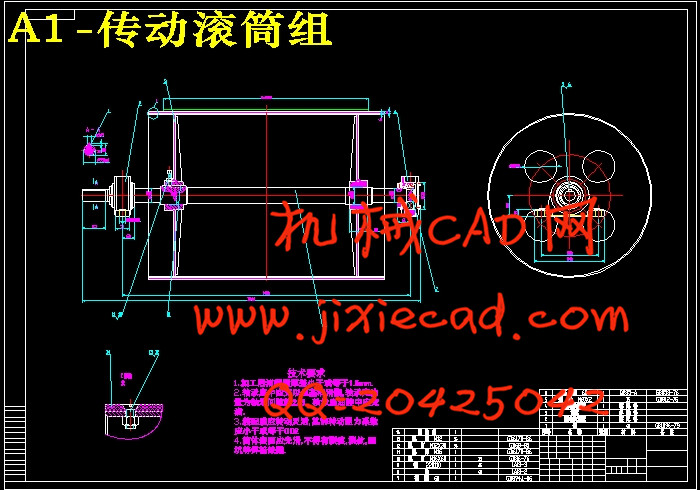
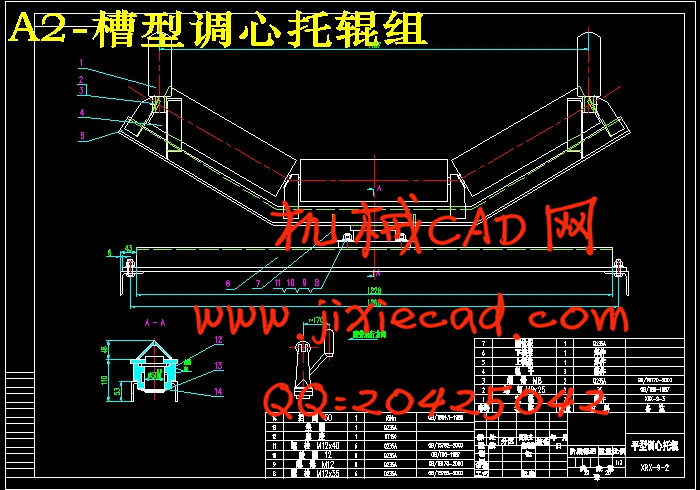
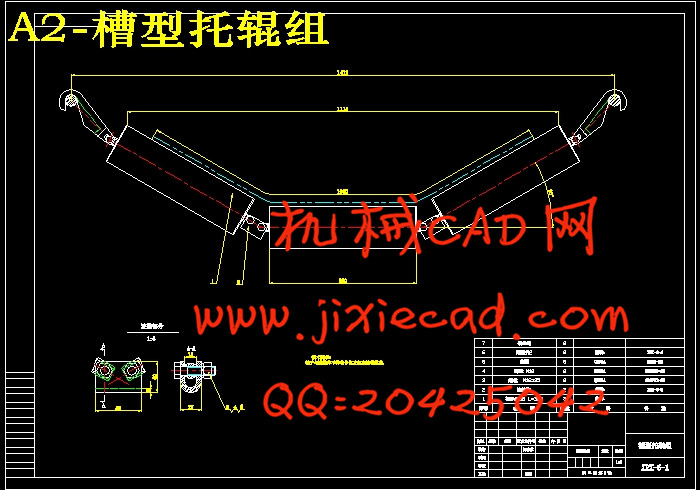
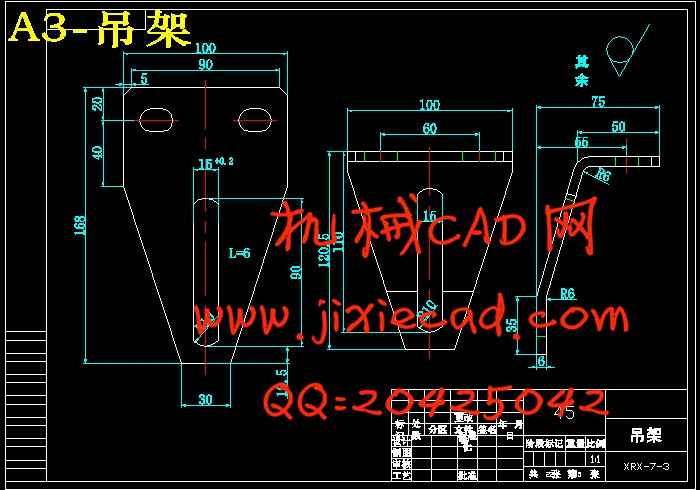
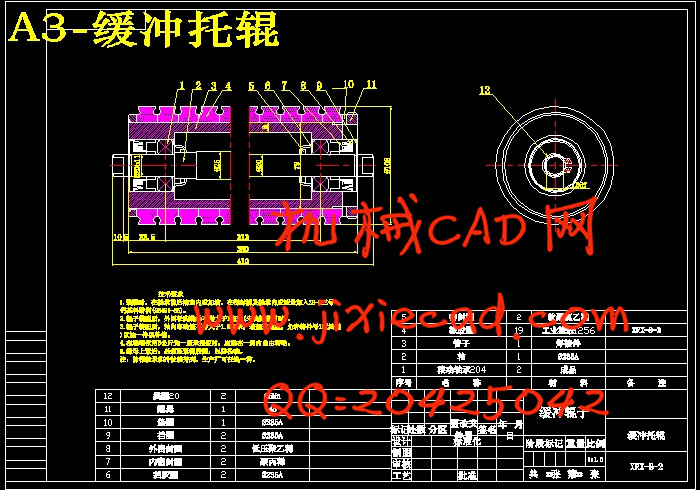
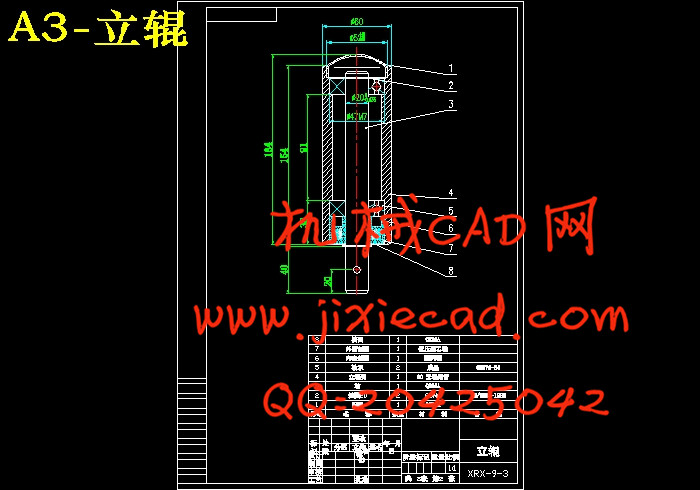
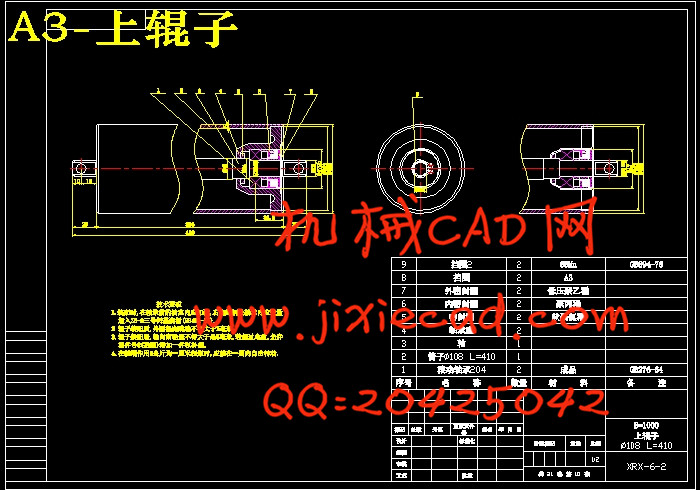
设计简介
摘 要
煤矿安全管理就是对煤矿安全生产相关要素和过程进行计划、组织、协调和控制的一系列活动, 以保障职工在生产过程中的生命安全, 保证生产工作的顺利开展, 保护国家和集体的财产不受损失。由于煤矿生产、管理工作中时时处处都与安全相联系,因此安全管理应该是全面的、全员的和全过程的, 是煤矿所有管理工作的核心。
管理要素是指管理活动和过程必不可少的组成部分。从煤矿安全管理的活动和过程看, 煤矿安全管理的要素主要包括人、物、环境三大要素。人是指员工的本体、意识和行为;物包括工程、设备、材料等硬件和技术、工艺、流程等软件两个方面;环境也包括硬件环境和软件环境两个方面, 硬件环境指由装备、技术等构成的生产、工作环境, 软件环境指由安全文化、宣传教育等构成的思想文化氛围。在人、物、环境诸因素中,人是最积极的因素,人既是安全管理的主体,也是安全管理的客体, 同时也是安全管理的直接目的-人的安全。而人的安全从狭义的角度也可以说是安全事故的承受者-决大部分生产一线员工的生命安全。
以人为本的管理思想是现代管理理念的主旋律。以人为本的管理是指任何管理都要以人为中心, 把提高人的素质、处理人际关系、满足人的需要、调动人的主动性、积极性、创造性的工作放在首位。因此在煤矿企业进行安全管理的时候,必须坚持以安全管理的主、客体, 对安全管理起着主导性作用的因素-人为根本, 立足于自身的意识、素质、能力的提高, 通过对外部其它管理要素物和环境的组织和控制影响作用与人, 从而实现安全生产。从安全管理的最直接的目的-人的安全来看, 安全管理中的“以人为本”管理思想应更多地倾向于生产一线的员工。
关键词:煤矿安全管理 要素分析 以人为本
ABSTRACT
煤矿安全管理就是对煤矿安全生产相关要素和过程进行计划、组织、协调和控制的一系列活动, 以保障职工在生产过程中的生命安全, 保证生产工作的顺利开展, 保护国家和集体的财产不受损失。由于煤矿生产、管理工作中时时处处都与安全相联系,因此安全管理应该是全面的、全员的和全过程的, 是煤矿所有管理工作的核心。
管理要素是指管理活动和过程必不可少的组成部分。从煤矿安全管理的活动和过程看, 煤矿安全管理的要素主要包括人、物、环境三大要素。人是指员工的本体、意识和行为;物包括工程、设备、材料等硬件和技术、工艺、流程等软件两个方面;环境也包括硬件环境和软件环境两个方面, 硬件环境指由装备、技术等构成的生产、工作环境, 软件环境指由安全文化、宣传教育等构成的思想文化氛围。在人、物、环境诸因素中,人是最积极的因素,人既是安全管理的主体,也是安全管理的客体, 同时也是安全管理的直接目的-人的安全。而人的安全从狭义的角度也可以说是安全事故的承受者-决大部分生产一线员工的生命安全。
以人为本的管理思想是现代管理理念的主旋律。以人为本的管理是指任何管理都要以人为中心, 把提高人的素质、处理人际关系、满足人的需要、调动人的主动性、积极性、创造性的工作放在首位。因此在煤矿企业进行安全管理的时候,必须坚持以安全管理的主、客体, 对安全管理起着主导性作用的因素-人为根本, 立足于自身的意识、素质、能力的提高, 通过对外部其它管理要素物和环境的组织和控制影响作用与人, 从而实现安全生产。从安全管理的最直接的目的-人的安全来看, 安全管理中的“以人为本”管理思想应更多地倾向于生产一线的员工。
关键词:煤矿安全管理 要素分析 以人为本
ABSTRACT
Coal mine safety management is to the coal mine safety production related elements and process planning, organization, coordination and control of a series of activities which guarantee a worker in production process of life safety, ensure the production work smoothly, protect national and collective property do not suffer loss. Due to the coal mine production and management work everywhere are associated with safety, so safety management should be comprehensive, all of our employees and whole process, is the core of all management work in the coal mine.
Management’s elements is refers to the indispensable part of management activities and process. Reference to the activities and processes of coal mine safety management, coal mine safety management elements include three elements: man, objects and environment. Man refers to the staff's ontology, consciousness and behavior; The things including two aspects, part of it is hardware such as engineering, equipment, materials and so on; the other part is software as technology, process, etc ; The environment also includes hardware and software environment in two aspects: the hardware environment refers to the equipment, technology of production, working environment; Software environment refers to the ideological and cultural atmosphere that is constituted by the security culture and publicity education. In these factors, man, content and environmental, man is the most active factor, the man is not only the main body of safety management, but also the object of safety management, and at the same time, the safety management of direct purpose - people's safety. While the human security from a narrow angle can also be said that the safety accident bear - most of the production line staff of life safety.
The idea of human-oriented management is a modern management philosophy theme. The people-oriented management refers to any management should be a center with the person. To improve the person's quality, interpersonal relationships, to meet the needs of the people, to arouse people's initiative, enthusiasm, creative work ,meanwhile, be a prime concern. Therefore, in the coal mining enterprises to carry out safety management, we must adhere to the man as the fundamental, based on their own consciousness, quality, ability, through the foreign ministry and other management, through the external other management elements, content and environmental, effect on organization and control to realize safety production. From safety management's the most direct purpose - human's safety, safety management in the "people-oriented" management idea should be more inclined to the staff of production line.
Keywords: coalmine safety management; analysis of elements; people first
目 录
第一章 绪论…………………………………………………………………………… 1Management’s elements is refers to the indispensable part of management activities and process. Reference to the activities and processes of coal mine safety management, coal mine safety management elements include three elements: man, objects and environment. Man refers to the staff's ontology, consciousness and behavior; The things including two aspects, part of it is hardware such as engineering, equipment, materials and so on; the other part is software as technology, process, etc ; The environment also includes hardware and software environment in two aspects: the hardware environment refers to the equipment, technology of production, working environment; Software environment refers to the ideological and cultural atmosphere that is constituted by the security culture and publicity education. In these factors, man, content and environmental, man is the most active factor, the man is not only the main body of safety management, but also the object of safety management, and at the same time, the safety management of direct purpose - people's safety. While the human security from a narrow angle can also be said that the safety accident bear - most of the production line staff of life safety.
The idea of human-oriented management is a modern management philosophy theme. The people-oriented management refers to any management should be a center with the person. To improve the person's quality, interpersonal relationships, to meet the needs of the people, to arouse people's initiative, enthusiasm, creative work ,meanwhile, be a prime concern. Therefore, in the coal mining enterprises to carry out safety management, we must adhere to the man as the fundamental, based on their own consciousness, quality, ability, through the foreign ministry and other management, through the external other management elements, content and environmental, effect on organization and control to realize safety production. From safety management's the most direct purpose - human's safety, safety management in the "people-oriented" management idea should be more inclined to the staff of production line.
Keywords: coalmine safety management; analysis of elements; people first
目 录
1.1 研究的背景……………………………………………………………………… 1
1.2 研究的意义……………………………………………………………………… 1
第二章 原始数据和工作条件………………………………………………… 3
2.1 原始数据和工作条件…………………………………………………………… 3
2.1.1 物料名称…………………………………………………………………… 3
2.1.2 物理性质…………………………………………………………………… 3
2.1.3 输送量……………………………………………………………………… 3
2.1.4 输送机布置形式及尺寸…………………………………………………… 3
2.1.5 卸料方式…………………………………………………………………… 3
2.1.6 工作环境…………………………………………………………………… 3
第三章 设计计算……………………………………………………………………… 5
3.1 带式输送机工作原理…………………………………………………………… 5
3.2 初选胶带输送机形式和布置…………………………………………………… 6
3.2.1 选型设计原则……………………………………………………………… 6
3.2.2 选型设计注意方面………………………………………………………… 6
3.2.3 初选胶带输送机形式……………………………………………………… 7
3.3 胶带宽度的计算………………………………………………………………… 7
3.3.1 初选带宽…………………………………………………………………… 7
3.3.2 带速的选择………………………………………………………………… 7
3.3.3 胶带宽度的计算…………………………………………………………… 8
3.3.4 胶带宽度的校核…………………………………………………………… 9
3.3.5 胶带输送量的验算……………………………………………………… 10
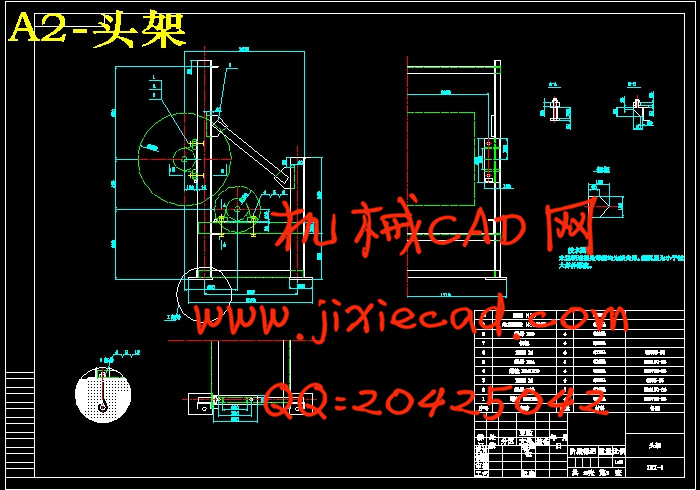
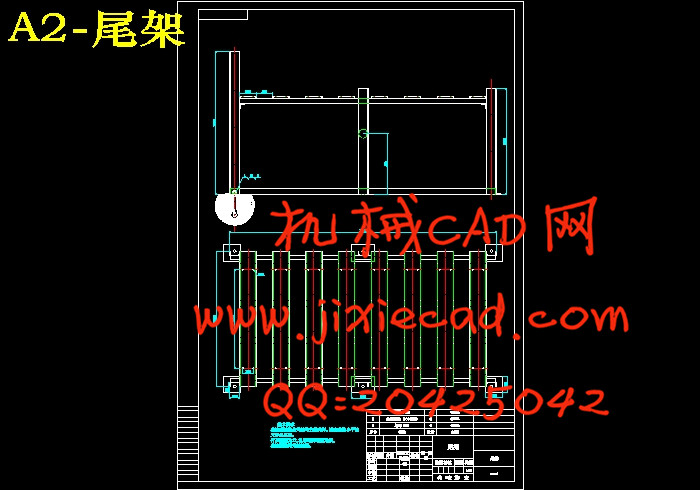
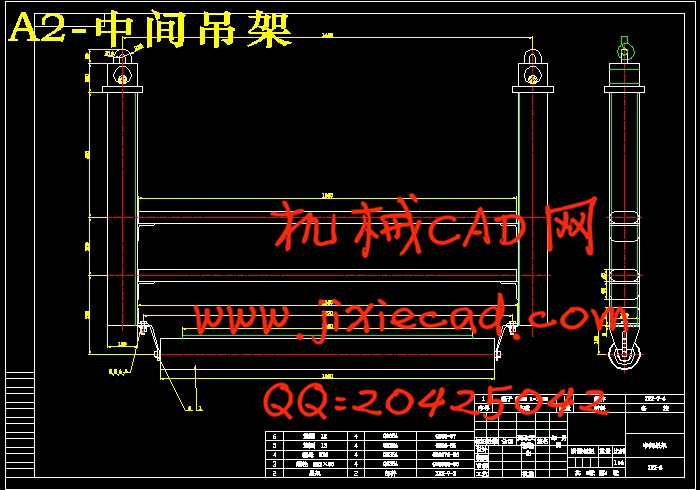
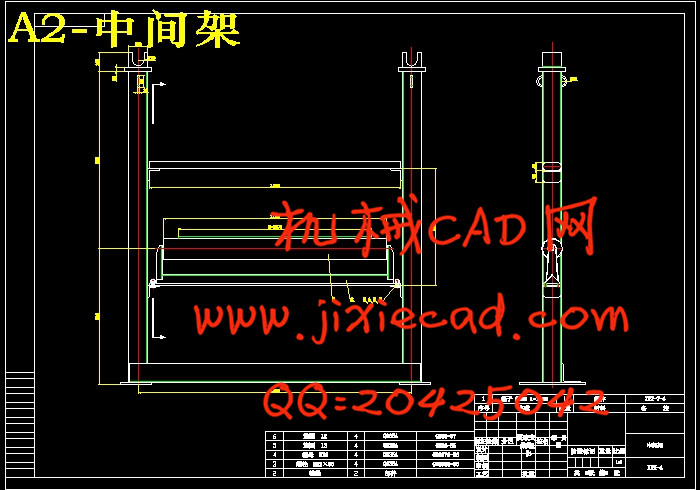
3.4 机头机尾结构和中间吊挂结构的选定和设计………………………………… 10
3.4.1 机架的设计准则………………………………………………………… 10
3.4.2 机架设计满足的要求…………………………………………………… 11
3.4.3 机头机架结构选择设计………………………………………………… 11
3.4.4 中间吊挂式结构的设计………………………………………………… 12
3.4.5 分绳架的设计…………………………………………………………… 13
3.4.6 中间吊架的设计………………………………………………………… 13
3.4.7 机尾结构的选择设计…………………………………………………… 13
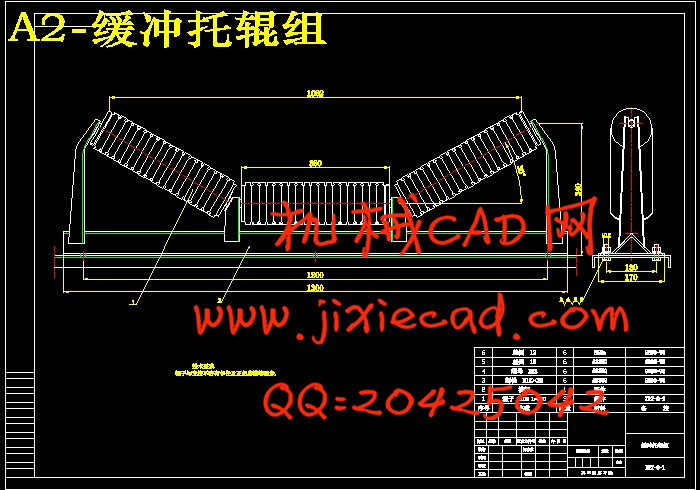
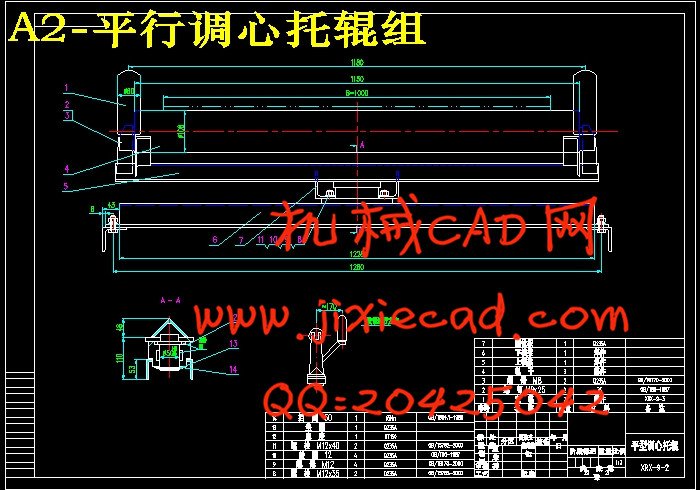
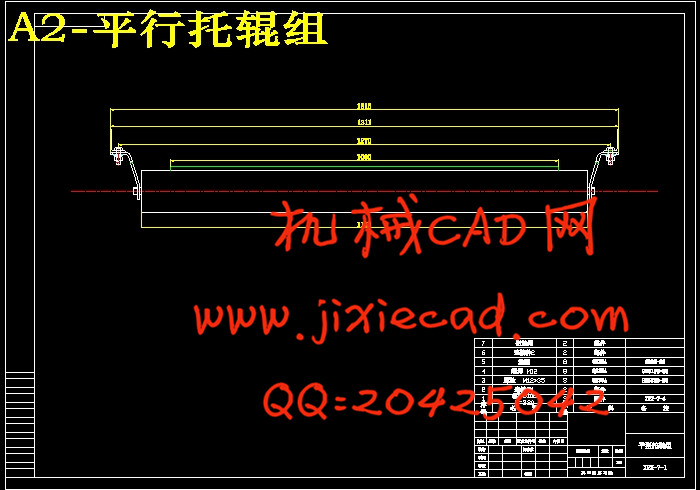
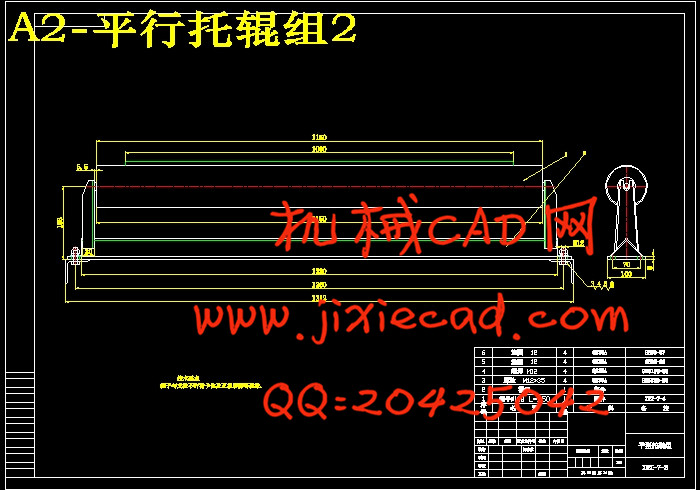
3.4.8 托辊的选择……………………………………………………………… 14
3.5 胶带的选择……………………………………………………………………… 16
3.5.1 胶带种类的选择………………………………………………………… 16
3.5.2 输送带的胶接方式……………………………………………………… 17
3.6 滚筒的选择……………………………………………………………………… 18
3.6.1 常用滚筒类型及特点分析……………………………………………… 18
3.6.2 滚筒的选择……………………………………………………………… 19
3.7 运行阻力的计算………………………………………………………………… 20
3.7.1 运行阻力计算…………………………………………………………… 20
3.7.2 附加运行阻力计算……………………………………………………… 22
3.8 胶带张力的计算………………………………………………………………… 24
3.8.1 带式输送机张力分布草图……………………………………………… 24
3.8.2 胶带张力计算…………………………………………………………… 24
3.8.3 验算胶带是否打滑……………………………………………………… 25
3.8.4 胶带强度验算…………………………………………………………… 25
3.9 悬垂度验算……………………………………………………………………… 26
3.9.1 胶带满足悬垂度条件的最小张力点计算……………………………… 26
3.10 电动机和减速器的选择计算………………………………………………… 27
3.10.1 传动滚筒牵引力计算…………………………………………………… 27
3.10.2 电动机功率计算………………………………………………………… 27
3.10.3 电动机的选择…………………………………………………………… 27
3.10.4 电动机布置方式………………………………………………………… 28
3.10.5 减速器的选择和计算…………………………………………………… 29
3.10.6 联轴器的选择…………………………………………………………… 29
3.11 偶合器的选择………………………………………………………………… 30
3.12 张紧装置的选择……………………………………………………………… 30
3.12.1 张紧装置的作用………………………………………………………… 30
3.12.2 张紧装置在使用中满足的要求………………………………………… 31
3.12.3 张紧装置在布局时应遵循的原则……………………………………… 31
3.12.4 常用的张紧装置………………………………………………………… 32
3.13 胶带输送机实际带速和实际输出量计算…………………………………… 33
3.13.1 胶带输送机实际带速的计算…………………………………………… 33
3.13.2 胶带输送机实际输出量的计算………………………………………… 33
3.14 自动调偏装置、清扫装置、保护设计的选择………………………………… 33
3.14.1 自动调偏装置的选择…………………………………………………… 33
3.14.2 清扫装置的选择………………………………………………………… 34
3.14.3 保护设计的选择………………………………………………………… 36
第四章 带式输送机操作及安全………………………………………………… 37
4.1 控制操作及安全……………………………………………………………… 37
4.1.1 设备联锁………………………………………………………………… 37
4.1.2 操作方式………………………………………………………………… 37
4.1.3 安全措施………………………………………………………………… 38
第五章 带式输送机常见故障发生及处理方法……………………………… 39
5.1 胶带输送机跑偏的原因及处理方法…………………………………………… 39
5.2 胶带输送机撤料的原因及处理方法…………………………………………… 40
5.3 控胶带打滑原因及处理办法…………………………………………………… 40
第六章 结论…………………………………………………………………………… 41
参考文献………………………………………………………………………………… 42
致谢……………………………………………………………………………………… 43