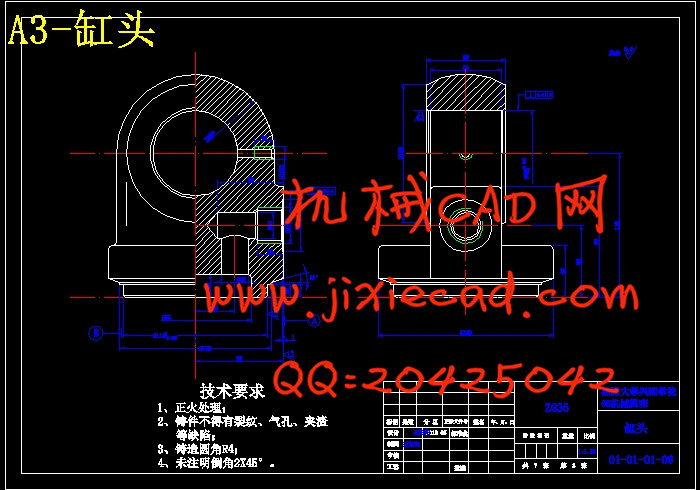
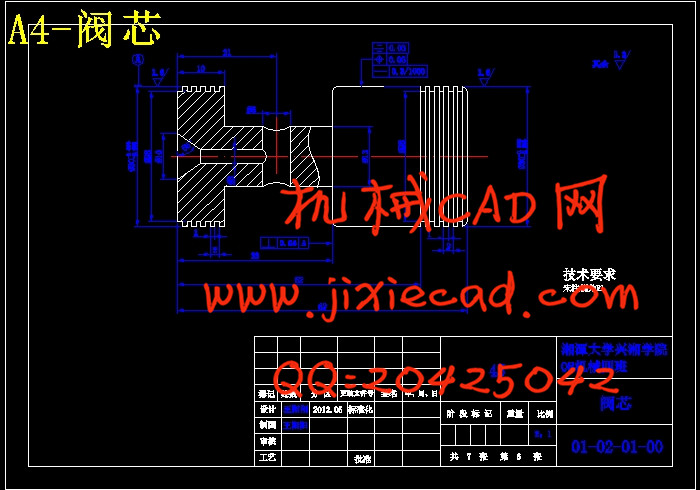
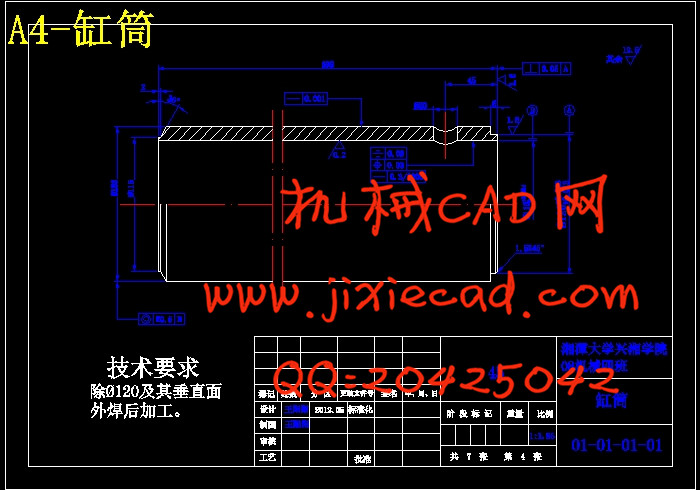
设计简介
目录
摘要 I
Abstract II
前 言 1
第一章 全液压轮式装载机液压系统的工作原理 2
1.1设计依据 2
1.1.1全液压轮式装载机液压系统的主要特点 2
1.1.2设计参数 2
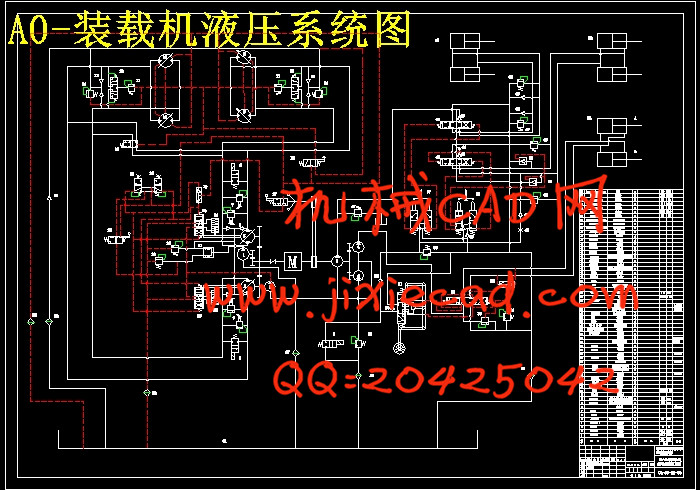
1.2全液压轮式装载机液压系统的工作原理 3
1.2.1行走机构液压系统 3
1.2.2工作装置液压系统 6
1.2.3转向机构液压系统 8
第二章 液压系统主要参数的确定 10
2.1行走机构液压系统若干问题 10
2.1.1液压泵参数的确定 10
2.1.2液压马达的参数 11
2.2铰接式车架的计算载荷 12
2.2.1两缸轴线至铰接点中心距离和行程确定 12
2.2.2转向泵流量 12
12
2.2.3最小转弯半径 12
2.3工作装置液压系统 13
2.3.1活塞直径和活塞杆直径的确定 13
2.3.2液压缸流量的计算 13
2.4原动机功率选择计算 14
2.4.1运输工况功率 14
2.4.2插入工况功率 15
第三章 非标准液压元件的设计 16
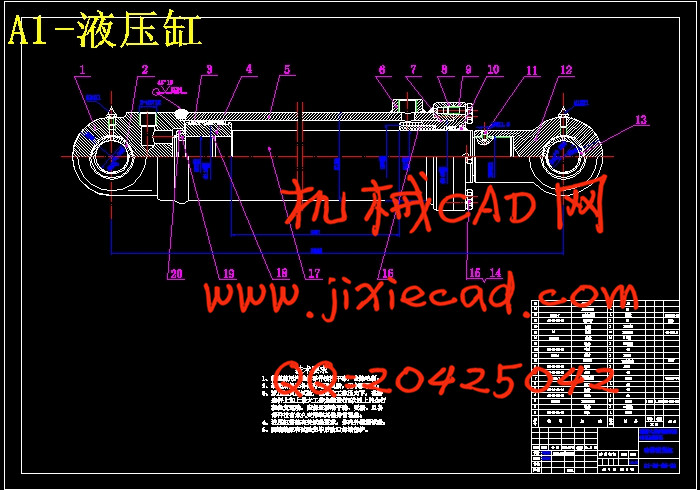
3.1动臂液压缸的设计 16
3.1.1液压缸的设计计算 16
3.1.2液压缸的作用能力、作用时间及储油量的计算 17
3.1.3液压缸壁厚的计算 18
3.1.4活塞杆的计算 18
3.1.5液压缸零件的连接计算 20
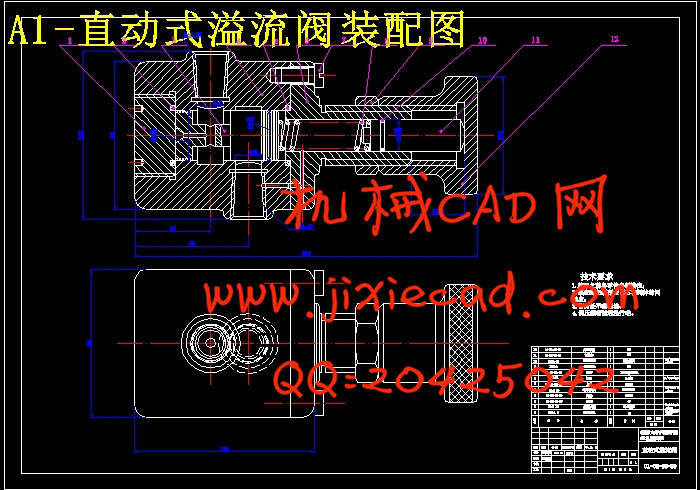
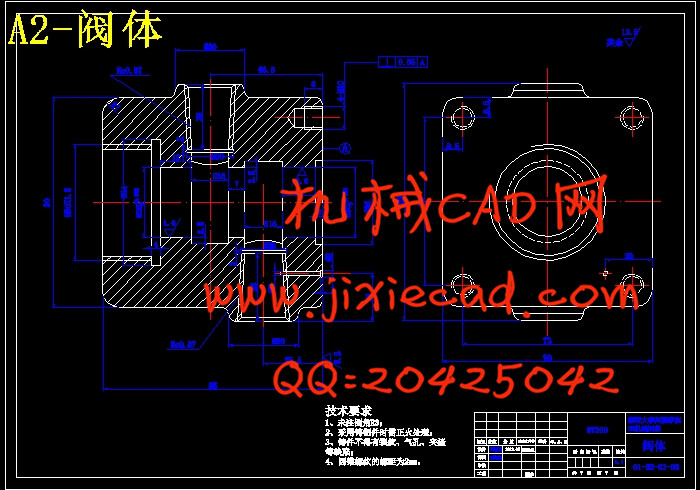
3.2直动式溢流阀的设计 23
3.2.1设计要求 23
3.2.2主要结构尺寸的初步确定 23
3.2.3静态特性计算 25
3.2.4弹簧的设计计算 26
第四章 结束语30
参考文献 31
全液压轮式装载机液压系统的设计摘要 I
Abstract II
前 言 1
第一章 全液压轮式装载机液压系统的工作原理 2
1.1设计依据 2
1.1.1全液压轮式装载机液压系统的主要特点 2
1.1.2设计参数 2
1.2全液压轮式装载机液压系统的工作原理 3
1.2.1行走机构液压系统 3
1.2.2工作装置液压系统 6
1.2.3转向机构液压系统 8
第二章 液压系统主要参数的确定 10
2.1行走机构液压系统若干问题 10
2.1.1液压泵参数的确定 10
2.1.2液压马达的参数 11
2.2铰接式车架的计算载荷 12
2.2.1两缸轴线至铰接点中心距离和行程确定 12
2.2.2转向泵流量
2.2.3最小转弯半径 12
2.3工作装置液压系统 13
2.3.1活塞直径和活塞杆直径的确定 13
2.3.2液压缸流量的计算 13
2.4原动机功率选择计算 14
2.4.1运输工况功率 14
2.4.2插入工况功率 15
第三章 非标准液压元件的设计 16
3.1动臂液压缸的设计 16
3.1.1液压缸的设计计算 16
3.1.2液压缸的作用能力、作用时间及储油量的计算 17
3.1.3液压缸壁厚的计算 18
3.1.4活塞杆的计算 18
3.1.5液压缸零件的连接计算 20
3.2直动式溢流阀的设计 23
3.2.1设计要求 23
3.2.2主要结构尺寸的初步确定 23
3.2.3静态特性计算 25
3.2.4弹簧的设计计算 26
第四章 结束语30
参考文献 31
——直动式溢流阀的设计
摘要
目前国内外的装载机广泛采用液压技术,可使整个装载机的技术经济指标得到提高。装载机主要用于装卸运作业。本设计的主要内容包括:工作装置液压系统、转向机构液压系统和行走机构液压系统的设计计算;标准液压元件的选择计算;液压系统的验算;非标件直动式溢流阀和动臂液压缸的设计计算。行走机构采用脚踏式操纵,先导控制的液控调速方式,使调速换向更为方便;工作装置采用先导控制,使系统操作更加简便;转向机构采用方向盘转向,运用人机学,使驾驶室的布置更为合理,便于操纵。整个系统安全可靠、结构紧凑和维修方便。
Abstract
Recently, the loader uses the hydraulic technology widely to make the target of its technological economy improved. The loader is used to do loading and unloading operation. This design includes the following aspects: the calculation of the design of the hydraulic system of equipment, steering gear, and running gear; the calculation of the design of nonstandard direct-acting overflow valve and the moving armed hydraulic cylinder. The running gear uses pedal control and the method of piloted pilot-operated speed governing to make the speed governing and reversing gear done much easier. The equipment uses the indirect control to make system operation much easier. The steering gear uses the changing direction of steering wheel and ergonomics to make the arrangement of the cab more suitable and easier to control. The whole system is more safe and reliable, the structure of which is tighter knit, and it is convenient to maintain.
Key words: loader, hydraulic system, hydraulic cylinder, direct-acting overflow valve