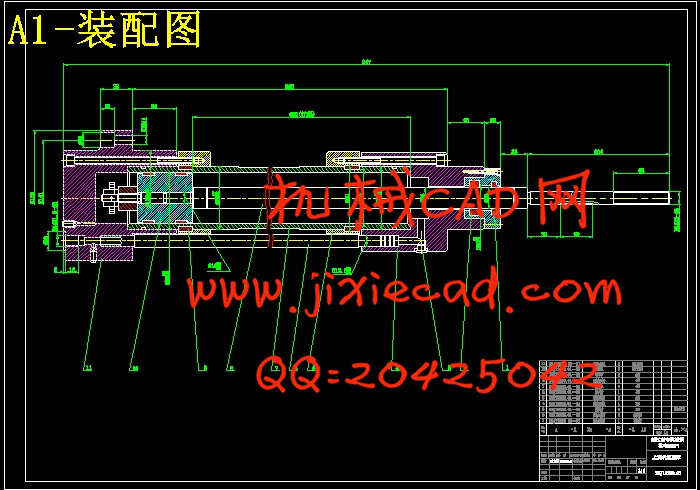
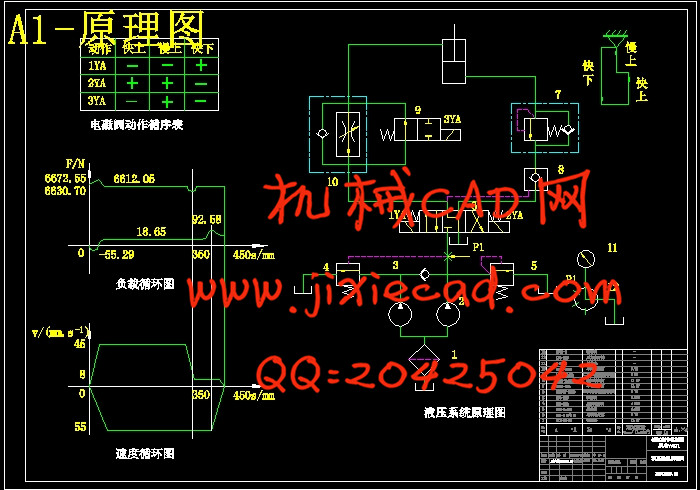
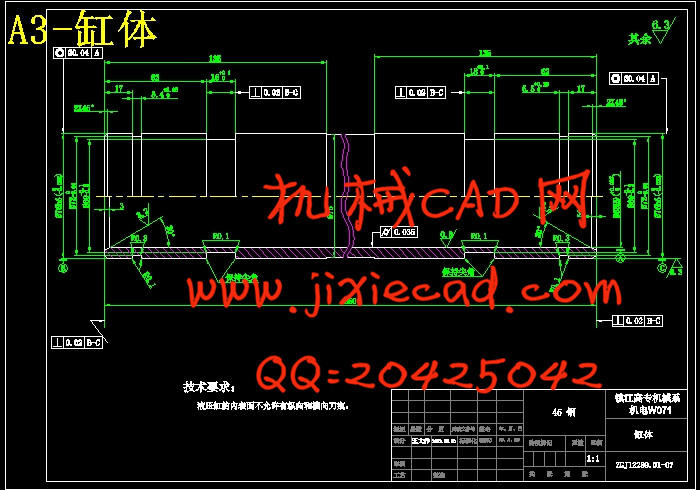
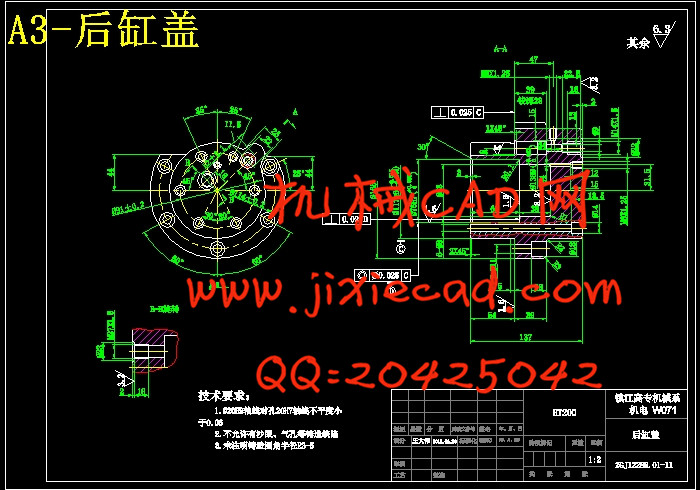
设计简介
摘要 液压作为一个广泛应用的技术,在未来更是有广阔的前景。随着计算机的深入发展,液压控制系统可以和智能控制的技术、计算机控制的技术等技术结合起来,这样就能够在更多的场合中发挥作用,也可以更加精巧的、更加灵活地完成预期的控制任务。
液压传动是流体传动的一种,其基本原理是在密闭的容器内,利用有压力的油液作为工作介质来实现能量转换和传递动力的。其中的液体称为工作介质,一般为矿物油,它的作用和机械传动中的皮带、链条和齿轮等传动元件相类似。
液压系统主要由:动力元件(油泵)、执行元件(油缸或液压马达)、控制元件(各种阀)、辅助元件和工作介质等五部分组成。
液压传动的优缺点
1、液压传动的优点
(1)体积小、重量轻,因此惯性力较小,当突然过载或停车时,不会发生大的冲击;
(2)能在给定范围内平稳的自动调节牵引速度,并可实现无极调速;
(3)换向容易,在不改变电机旋转方向的情况下,可以较方便地实现工作机构旋转和直线往复运动的转换;
(4)液压泵和液压马达之间用油管连接,在空间布置上彼此不受严格限制;
(5)由于采用油液为工作介质,元件相对运动表面间能自行润滑,磨损小,使用寿命长;
(6)操纵控制简便,自动化程度高;
(7)容易实现过载保护。
2、液压传动的缺点
(1)使用液压传动对维护的要求高,工作油要始终保持清洁;
(2)对液压元件制造精度要求高,工艺复杂,成本较高;
(3)液压元件维修较复杂,且需有较高的技术水平;
(4)用油做工作介质,在工作面存在火灾隐患;
(5)传动效率低。
关键词 液压缸 活塞杆 验算 供油 调速
Feeder hydraulic system design
Abstract The modern machinery general many is mechanical, electrical, hydraulic three closely and combination of a complex structure. Hydraulic drive and mechanical transmission, electrical transmission and classified as three traditional form, hydraulic transmission system design in the modern mechanical design work occupies an important position. So, choose hydraulic transmission subject topics as the graduation design issue is of engineering machinery of various kinds of common choice. Hydraulic transmission technology is not only a theoretical very strong technology, and with the actual production has the close relation. In order to learn such an important technology, in addition to teaching system in teaching, but also can be used as the graduation design teaching, through the theory with practice, to grasp the hydraulic transmission system design skills and methods.
Hydraulic transmission of graduation design goal mainly have the following:
1 and comprehensive application of hydraulic drive course and other relevant courses theoretical knowledge and practical knowledge production, hydraulic transmission design practice, is the theoretical knowledge and production practice in close integration with, so that this knowledge to further consolidate, deepen improve and expand.
2 in the design practice, learn and master general hydraulic components, especially the of all kinds of standard component selection principle and method of the loop combination, training design skills, improve the student analysis and the actual production of grafting question ability, the design work for the future lay a good foundation.
3, through the design, further familiar with design data (including design manual, product samples, standards and specification) apply, and improve the calculation, drawing (CAD), and experience the ability to estimate.
4, cultivating their own autonomous learning, practical and team cooperation ability.
Key words hydraulic cylinder piston energy supply speed
目 录
摘要 …………………………………………………………………………………………3
引言 …………………………………………………………………………………………5
上料机的液压系统设计……………………………………………………6
1.1设计要求…………………………………………………………………6
1.2负载分析…………………………………………………………………………6
1.2.1 工作负载……………………………………………………………………6
1.2.2 摩擦负载……………………………………………………………………6
1.2.3 惯性负载……………………………………………………………………7
1.3 负载图和速度图的绘制……………………………………………………8
1.4液压缸主要参数的确定……………………………………………………9
1.4.1初选液压缸的工作压力………………………………………………9
1.4.2计算液压缸的尺寸……………………………………………………9
1.4.3活塞杆稳定性校核………………………………………………………10
1.4.4求液压缸的最大流量………………………………………………………10
1.4.5 绘制工况图………………………………………………………………11
1.5液压系统图的拟定……………………………………………………………12
1.6液压元件的选用…………………………………………………………………13
1.6.1确定液压泵的型号及电动机功率…………………………………………13
1.6.2选择阀类元件及辅助元件…………………………………………………14
1.7液压系统的性能验算…………………………………………………………15
1.7.1压力损失及调定压力的确定………………………………………………15
1.7.2系统的发热与温升…………………………………………………………17
第二章 液压缸…………………………………………………………………………18
2.1液压缸的介绍………………………………………………………………………18
2.2液压缸主要参数的确定……………………………………………………………20
2.2.1 液压缸工作压力……………………………………………………………20
2.2.2 液压缸的长度和壁厚的确定………………………………………………20
2.2.3 液压缸进出油口尺寸的计算………………………………………………21
2.3 液压缸的结构设计…………………………………………………………21
2.3.1液压缸的连接………………………………………………………………21
2.3.2活塞与缸体的密封形式……………………………………………………22
2.3.3液压缸的辅助设置………………………………………………………22
2.4液压缸零件的技术要求……………………………………………………23
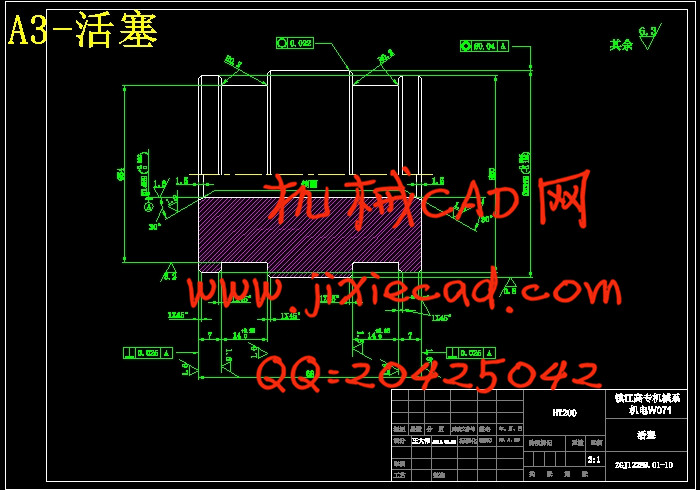
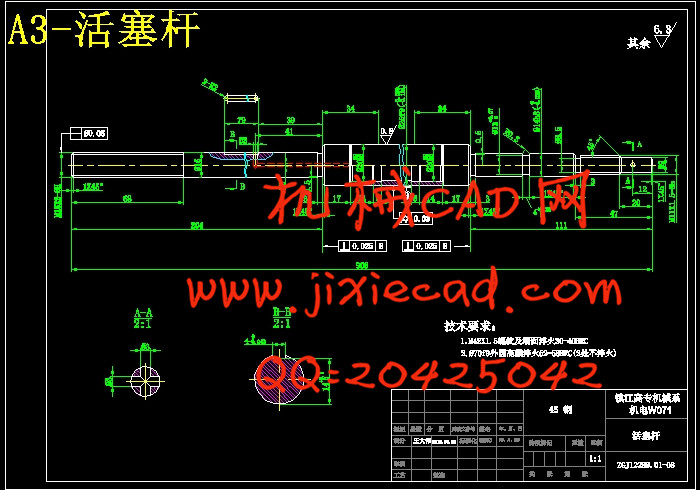
2.4.1活塞杆……………………………………………………………………23
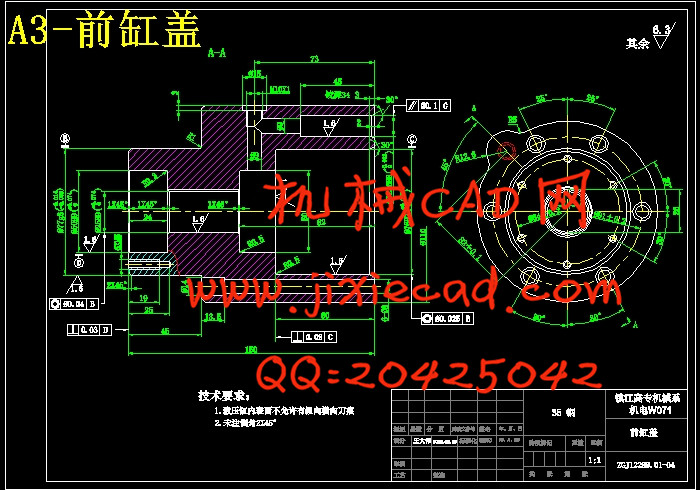
2.4.2缸体……………………………………………………………………23
2.4.3活塞……………………………………………………………………24
结论…………………………………………………………………………………………25
致谢…………………………………………………………………………………26
参考文献……………………………………………………………………………27
液压传动是流体传动的一种,其基本原理是在密闭的容器内,利用有压力的油液作为工作介质来实现能量转换和传递动力的。其中的液体称为工作介质,一般为矿物油,它的作用和机械传动中的皮带、链条和齿轮等传动元件相类似。
液压系统主要由:动力元件(油泵)、执行元件(油缸或液压马达)、控制元件(各种阀)、辅助元件和工作介质等五部分组成。
液压传动的优缺点
1、液压传动的优点
(1)体积小、重量轻,因此惯性力较小,当突然过载或停车时,不会发生大的冲击;
(2)能在给定范围内平稳的自动调节牵引速度,并可实现无极调速;
(3)换向容易,在不改变电机旋转方向的情况下,可以较方便地实现工作机构旋转和直线往复运动的转换;
(4)液压泵和液压马达之间用油管连接,在空间布置上彼此不受严格限制;
(5)由于采用油液为工作介质,元件相对运动表面间能自行润滑,磨损小,使用寿命长;
(6)操纵控制简便,自动化程度高;
(7)容易实现过载保护。
2、液压传动的缺点
(1)使用液压传动对维护的要求高,工作油要始终保持清洁;
(2)对液压元件制造精度要求高,工艺复杂,成本较高;
(3)液压元件维修较复杂,且需有较高的技术水平;
(4)用油做工作介质,在工作面存在火灾隐患;
(5)传动效率低。
关键词 液压缸 活塞杆 验算 供油 调速
Feeder hydraulic system design
Abstract The modern machinery general many is mechanical, electrical, hydraulic three closely and combination of a complex structure. Hydraulic drive and mechanical transmission, electrical transmission and classified as three traditional form, hydraulic transmission system design in the modern mechanical design work occupies an important position. So, choose hydraulic transmission subject topics as the graduation design issue is of engineering machinery of various kinds of common choice. Hydraulic transmission technology is not only a theoretical very strong technology, and with the actual production has the close relation. In order to learn such an important technology, in addition to teaching system in teaching, but also can be used as the graduation design teaching, through the theory with practice, to grasp the hydraulic transmission system design skills and methods.
Hydraulic transmission of graduation design goal mainly have the following:
1 and comprehensive application of hydraulic drive course and other relevant courses theoretical knowledge and practical knowledge production, hydraulic transmission design practice, is the theoretical knowledge and production practice in close integration with, so that this knowledge to further consolidate, deepen improve and expand.
2 in the design practice, learn and master general hydraulic components, especially the of all kinds of standard component selection principle and method of the loop combination, training design skills, improve the student analysis and the actual production of grafting question ability, the design work for the future lay a good foundation.
3, through the design, further familiar with design data (including design manual, product samples, standards and specification) apply, and improve the calculation, drawing (CAD), and experience the ability to estimate.
4, cultivating their own autonomous learning, practical and team cooperation ability.
Key words hydraulic cylinder piston energy supply speed
目 录
摘要 …………………………………………………………………………………………3
引言 …………………………………………………………………………………………5
上料机的液压系统设计……………………………………………………6
1.1设计要求…………………………………………………………………6
1.2负载分析…………………………………………………………………………6
1.2.1 工作负载……………………………………………………………………6
1.2.2 摩擦负载……………………………………………………………………6
1.2.3 惯性负载……………………………………………………………………7
1.3 负载图和速度图的绘制……………………………………………………8
1.4液压缸主要参数的确定……………………………………………………9
1.4.1初选液压缸的工作压力………………………………………………9
1.4.2计算液压缸的尺寸……………………………………………………9
1.4.3活塞杆稳定性校核………………………………………………………10
1.4.4求液压缸的最大流量………………………………………………………10
1.4.5 绘制工况图………………………………………………………………11
1.5液压系统图的拟定……………………………………………………………12
1.6液压元件的选用…………………………………………………………………13
1.6.1确定液压泵的型号及电动机功率…………………………………………13
1.6.2选择阀类元件及辅助元件…………………………………………………14
1.7液压系统的性能验算…………………………………………………………15
1.7.1压力损失及调定压力的确定………………………………………………15
1.7.2系统的发热与温升…………………………………………………………17
第二章 液压缸…………………………………………………………………………18
2.1液压缸的介绍………………………………………………………………………18
2.2液压缸主要参数的确定……………………………………………………………20
2.2.1 液压缸工作压力……………………………………………………………20
2.2.2 液压缸的长度和壁厚的确定………………………………………………20
2.2.3 液压缸进出油口尺寸的计算………………………………………………21
2.3 液压缸的结构设计…………………………………………………………21
2.3.1液压缸的连接………………………………………………………………21
2.3.2活塞与缸体的密封形式……………………………………………………22
2.3.3液压缸的辅助设置………………………………………………………22
2.4液压缸零件的技术要求……………………………………………………23
2.4.1活塞杆……………………………………………………………………23
2.4.2缸体……………………………………………………………………23
2.4.3活塞……………………………………………………………………24
结论…………………………………………………………………………………………25
致谢…………………………………………………………………………………26
参考文献……………………………………………………………………………27