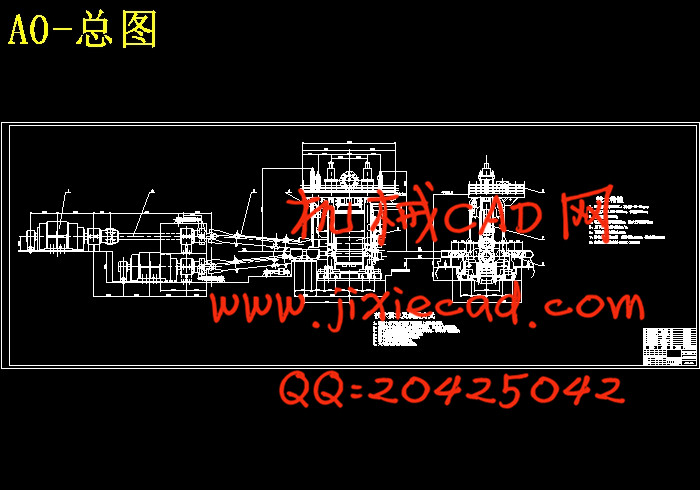
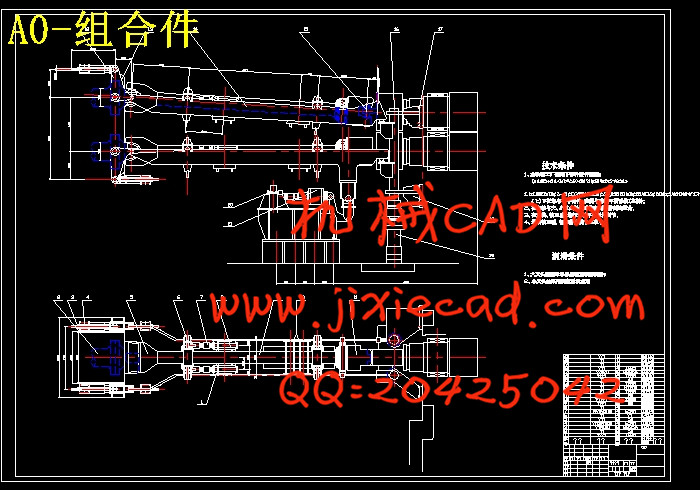
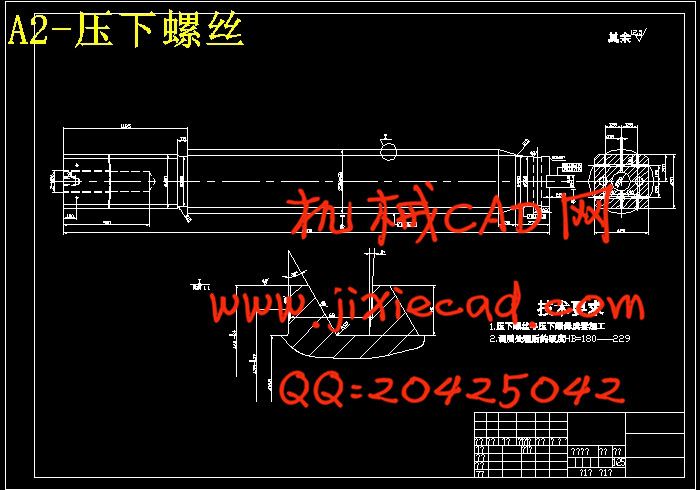
设计简介
方板坯开坯轧机设计
摘要
方、板坯开坯轧机既可轧制板坯,又可轧制方坯,生产比较灵活。又称为大开口度二辊可逆式初轧机。
初轧机的主要技术性能有:辊径为1150~1350mm,辊身长度为3100mm,轧辊的工作行程为1700mm,最大行程为1905mm,轧制压力为3000T,电动机功率5000 2KW,转速0~35~70rpm,压下速度为142~284mm/sec,两牌坊中心矩为4140mm,牌坊窗口开口度操作侧为1400mm,传动侧为1390mm。
2KW,转速0~35~70rpm,压下速度为142~284mm/sec,两牌坊中心矩为4140mm,牌坊窗口开口度操作侧为1400mm,传动侧为1390mm。
此轧机的设计包括轧制力的计算,电机容量的选择,压下系统的选择,压下螺丝、螺母尺寸的确定,压下电机的选择,平衡方法的计算,轧辊、万向连轴器、机架、轧辊轴承、齿轮、压下螺丝、螺母等主要零件的强度校核,以及润滑方法的选择,对控制系统的要求,设备的可靠性分析等内容。
初轧机较多地采用了液压传动,机械化程度比较高。
关键词 初轧机,轧制力,压下系统
Square billet and board billet bloomer s design
s design
Abstract
Square billet and board billet bloomer since can roll square billet and board billet,produce more vivid,is called again big openings degree two reollrs go against type rolling mill.
Main technique function of the bloomer: diameter of the roller is 1150mm~1350mm, corporeity of the roller is 3100mm, the work route of travel is 1700mm, the biggest route of travel is 1905mm,the rolling pressure is 3000T, electric motor power is 5000 2KW, the rotate speed is 0~35~70 rpm, the depressive speed is 142~284 mm/sec, the center distance of two toriis is 4140mm, openings degree of the toriis window: the operate profile is1400mm,the transmission profile is 1390mm.
2KW, the rotate speed is 0~35~70 rpm, the depressive speed is 142~284 mm/sec, the center distance of two toriis is 4140mm, openings degree of the toriis window: the operate profile is1400mm,the transmission profile is 1390mm.
The design of this rolling mill include the count of the rolling force,the choice of the electromotor capacitance, the choice of the depressive system, make certain the size of the depressive screm and nut, the choice of the depressive electromotor, the count of the balance means, verify the strength of the roller、the universal coupling、the machine shelf、the roller bearings、the wheel gear、the depressive screm and nut ect..And the choice of the lubricating means,the demand of the contral system,the dependability analyse of the equipment ect.
Bloomer adopte the liquid drive morely, mechanisation degree is higher.
Descriptors bloomer,rolling force,depressive system
目录
1 概述·······························································1
1.1初轧机在轧钢生产中的作用··········································1
1.2初轧机的分类······················································1
1.3初轧机在生产中存在的问题··········································2
1.4方案的选择和评述··················································2
2 初轧机力能参数的计算···············································5
2.1轧制规程 ·························································5
2.2轧辊主要参数的确当················································5
2.2.1 轧辊的名义直径··················································5
2.2.2 辊身长度························································5
2.2.3 辊颈直径和长度··················································5
2.3轧制力的计算······················································6
2.3.1 平均单位压力的计算··············································6
2.3.2 轧制力P的计算··················································9
2.4电机容量的选择····················································9
2.4.1 初选电机的容量··················································9
2.4.2电机轴上的力矩··················································11
2.4.3电机容量的校核··················································17
3.压下系统的计算·····················································19
3.1 压下螺丝和螺母尺寸的确定·········································19
3.2 压下系统的选择···················································19
3.2.1 1300初轧机的工艺特点···········································19
3.2.2压下系统的选择··················································19
3.2.3压下装置示意图··················································19
3.3 转动压下螺丝的力矩···············································20
4平衡力的计算·······················································23
4.1 平衡方法的确定···················································23
4.2 平衡力的计算·····················································23
5主要零件的强度计算·················································24
5.1 轧辊的强度计算···················································24
5.2 万向接轴的强度计算···············································26
5.2.1开口式扁头的受力分析和强度计算··································26
5.2.2叉头受力分析和强度计算··········································28
5.2.3轴体的强度计算··················································29
5.3 机架的强度计算···················································30
5.3.1机架的受力分析··················································30
5.3.2立柱、横梁的惯性矩和断面系数的计算······························31
5.3.3横梁和立柱的强度计算············································34
5.4 轧辊轴承的计算···················································36
5.5 齿轮的计算·······················································36
5.6 压下辊螺母和螺丝的强度校核·······································41
5.6.1压下螺母的强度校核··············································41
5.6.2压下螺丝的强度校核··············································42
6润滑方法的选择·····················································44
6.1 轧辊轴承的润滑···················································44
6.2 万向接轴的润滑···················································44
6.2.1并合环式润滑····················································44
6.2.2稀油喷雾润滑装置················································45
6.3 压下螺母和压下螺丝的润滑·········································45
6.4 齿轮的润滑·······················································45
7对控制系统的要求···················································46
7.1 压下传动装置·····················································46
7.2 轧辊·····························································46
7.3 下轧辊调整装置···················································46
7.4 低速传动装置·····················································46
8设备的可靠性分析···················································47
8.1 设备的平均寿命···················································47
8.2 设备的有效度·····················································47
8.3 设备的经济寿命···················································47
结论·································································48
致谢·································································49
参考文献·····························································50
附录·································································51
摘要
方、板坯开坯轧机既可轧制板坯,又可轧制方坯,生产比较灵活。又称为大开口度二辊可逆式初轧机。
初轧机的主要技术性能有:辊径为1150~1350mm,辊身长度为3100mm,轧辊的工作行程为1700mm,最大行程为1905mm,轧制压力为3000T,电动机功率5000
此轧机的设计包括轧制力的计算,电机容量的选择,压下系统的选择,压下螺丝、螺母尺寸的确定,压下电机的选择,平衡方法的计算,轧辊、万向连轴器、机架、轧辊轴承、齿轮、压下螺丝、螺母等主要零件的强度校核,以及润滑方法的选择,对控制系统的要求,设备的可靠性分析等内容。
初轧机较多地采用了液压传动,机械化程度比较高。
关键词 初轧机,轧制力,压下系统
Square billet and board billet bloomer
Abstract
Square billet and board billet bloomer since can roll square billet and board billet,produce more vivid,is called again big openings degree two reollrs go against type rolling mill.
Main technique function of the bloomer: diameter of the roller is 1150mm~1350mm, corporeity of the roller is 3100mm, the work route of travel is 1700mm, the biggest route of travel is 1905mm,the rolling pressure is 3000T, electric motor power is 5000
The design of this rolling mill include the count of the rolling force,the choice of the electromotor capacitance, the choice of the depressive system, make certain the size of the depressive screm and nut, the choice of the depressive electromotor, the count of the balance means, verify the strength of the roller、the universal coupling、the machine shelf、the roller bearings、the wheel gear、the depressive screm and nut ect..And the choice of the lubricating means,the demand of the contral system,the dependability analyse of the equipment ect.
Bloomer adopte the liquid drive morely, mechanisation degree is higher.
Descriptors bloomer,rolling force,depressive system
目录
1 概述·······························································1
1.1初轧机在轧钢生产中的作用··········································1
1.2初轧机的分类······················································1
1.3初轧机在生产中存在的问题··········································2
1.4方案的选择和评述··················································2
2 初轧机力能参数的计算···············································5
2.1轧制规程 ·························································5
2.2轧辊主要参数的确当················································5
2.2.1 轧辊的名义直径··················································5
2.2.2 辊身长度························································5
2.2.3 辊颈直径和长度··················································5
2.3轧制力的计算······················································6
2.3.1 平均单位压力的计算··············································6
2.3.2 轧制力P的计算··················································9
2.4电机容量的选择····················································9
2.4.1 初选电机的容量··················································9
2.4.2电机轴上的力矩··················································11
2.4.3电机容量的校核··················································17
3.压下系统的计算·····················································19
3.1 压下螺丝和螺母尺寸的确定·········································19
3.2 压下系统的选择···················································19
3.2.1 1300初轧机的工艺特点···········································19
3.2.2压下系统的选择··················································19
3.2.3压下装置示意图··················································19
3.3 转动压下螺丝的力矩···············································20
4平衡力的计算·······················································23
4.1 平衡方法的确定···················································23
4.2 平衡力的计算·····················································23
5主要零件的强度计算·················································24
5.1 轧辊的强度计算···················································24
5.2 万向接轴的强度计算···············································26
5.2.1开口式扁头的受力分析和强度计算··································26
5.2.2叉头受力分析和强度计算··········································28
5.2.3轴体的强度计算··················································29
5.3 机架的强度计算···················································30
5.3.1机架的受力分析··················································30
5.3.2立柱、横梁的惯性矩和断面系数的计算······························31
5.3.3横梁和立柱的强度计算············································34
5.4 轧辊轴承的计算···················································36
5.5 齿轮的计算·······················································36
5.6 压下辊螺母和螺丝的强度校核·······································41
5.6.1压下螺母的强度校核··············································41
5.6.2压下螺丝的强度校核··············································42
6润滑方法的选择·····················································44
6.1 轧辊轴承的润滑···················································44
6.2 万向接轴的润滑···················································44
6.2.1并合环式润滑····················································44
6.2.2稀油喷雾润滑装置················································45
6.3 压下螺母和压下螺丝的润滑·········································45
6.4 齿轮的润滑·······················································45
7对控制系统的要求···················································46
7.1 压下传动装置·····················································46
7.2 轧辊·····························································46
7.3 下轧辊调整装置···················································46
7.4 低速传动装置·····················································46
8设备的可靠性分析···················································47
8.1 设备的平均寿命···················································47
8.2 设备的有效度·····················································47
8.3 设备的经济寿命···················································47
结论·································································48
致谢·································································49
参考文献·····························································50
附录·································································51