设计简介
摘 要
点焊机器人【spot welding robot】 用于点焊自动作业的工业机器人。世界上第一台点焊机于1965年开始使用,是美国Unimation公司推出的Unimate机器人,中国在1987年自行研制成第一台点焊机器人──华宇-Ⅰ型点焊机器人。点焊机器人由机器人本体、计算机控制系统、示教盒和点焊焊接系统几部分组成,由于为了适应灵活动作的工作要求,通常电焊机器人选用关节式工业机器人的基本设计,一般具有六个自由度:腰转、大臂转、小臂转、腕转、腕摆及腕捻。其驱动方式有液压驱动和电气驱动两种。其中电气驱动具有保养维修简便、能耗低、速度高、精度高、安全性好等优点,因此应用较为广泛。点焊机器人按照示教程序规定的动作、顺序和参数进行点焊作业,其过程是完全自动化的,并且具有与外部设备通信的接口,可以通过这一接口接受上一级主控与管理计算机的控制命令进行工作。机器人点焊电极修磨器整个装置由电机通过二级减速装置带动锥齿轮运动,从而实现刀具的旋转和切削,同时利用“行星齿轮可以实现变速”的原理实现电极的粗削和精削,另外,可调式支架能够轻松的控制装置的高度。从而保证装置的高效性和实用性。
NGW型行星齿轮传动机构的传动原理:当高速轴由电机驱动,带动太阳轮,然后带动行星轮转动,内齿圈固定,然后带动行星架输出运动的,在行星架上的行星轮既自转和公转,具有相同的结构。二级,三级或多级传输。NGW型行星齿轮传动机构主要由太阳齿轮,行星齿轮,内齿圈,行星架,命名为基本成分后,也被称为zk-h型行星齿轮传动机构。
关键词: 行星齿轮减速器、运动仿真、装配、三维建模
Abstract
Spot welding robot] [spot welding robot automatic spot welding robots for industrial jobs. The world's first welder in 1965 started, the United States launched the Unimate Unimation robot, China in 1987 developed into the first spot welding robot ── Arima -Ⅰ type spot welding robots. Spot welding robots, robot consists of several parts of the body computer control system, teach pendant and spot welding system, because in order to meet work requirements and flexible action, usually welding robot use of basic design articulated industrial robots, typically with six degrees of freedom : turn back, the arm turn, turn arm, wrist rotation, and wrist twisting the wrist swing. Which drive a hydraulic drive and electric drive in two. Wherein the electric drive with a simple maintenance, low energy consumption, high speed, high precision, security and good benefits, and therefore is widely used. Spot welding robot teaching program in accordance with the provisions of the action, sequence and parameters of spot welding, the process is fully automated and has an interface to communicate with an external device, you can accept the level of the interface on the host computer and management control command to work.Robot spot welding electrode grinding is the entire device by a motor driven by a secondary bevel gear reduction device so as to perform rotation and cutting tools, while using the principle of "planet gear shift can be achieved," the realization of roughing and finishing cutting electrode, and the other Adjustable brackets can easily control the height of the apparatus. In order to ensure efficient and practical means.
NGW planetary gear transmission principle transmission mechanism: When the high speed shaft driven by a motor to drive the sun gear, and then drive the planetary gear rotates, the ring gear fixed, then the carrier output drive movement, both in the rotation and the planet carrier of the planetary gear revolution, has the same structure. Two, three or more stages of transmission. After NGW planetary gear mechanism consists of a sun gear, a planetary gear, ring gear, planet carrier, named as the basic component, also called zk-h type planetary gear mechanism.
Keywords: planetary gear reducer, assembly, motion simulation, 3D modeling
目 录
摘 要 II
Abstract III
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 点焊机器人介绍及其研究意义 1
1.2 工业机器人发展现状及趋势 1
1.2.1工业机器人发展现状 1
1.2.2 工业机器人发展趋势 2
1.3 国内外研究现状 3
1.4 主要的工作内容 4
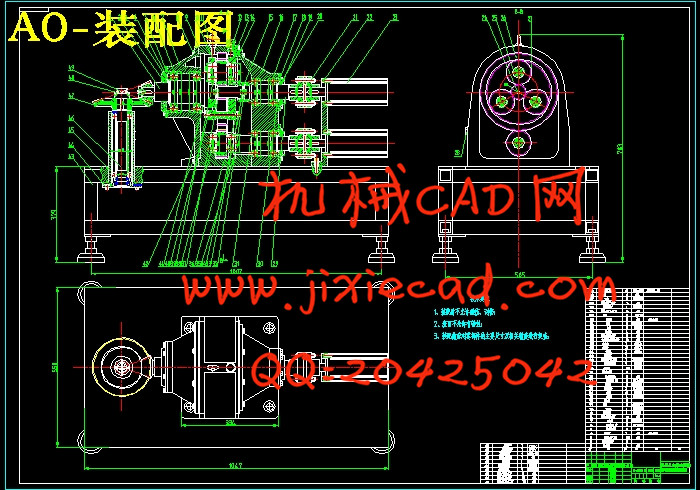
第2章 机器人点焊电极修磨器总体设计 5
2.1 机器人点焊电极修磨器简介 5
2.2 机器人点焊电极修磨器方案说明 5
2.3 设计总体方案 6
2.3.1 电阴点焊电极的基本介绍 6
2.3.2 刀具的设计 7
第3章 行星减速器结构设计 11
3.1 行星齿轮减速器的工作过程和结构机构简图的确定 11
3.2 周转轮系部分的选择 11
3.3 NGW型行星轮减速器方案确定 11
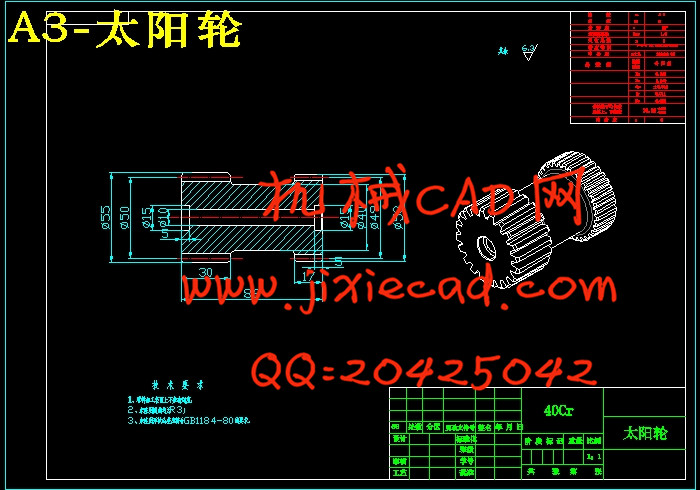
3.4 行星轮系中各轮齿数的确定 13
3.5 基本参数要求与选择 15
3.6 方案设计 17
3.6.1 机构简图 17
3.6.2 齿形及精度 17
3.6.3 齿轮材料及性能 18
3.7 齿轮的计算与校核 18
3.7.1 配齿数 18
3.7.2 初步计算齿轮主要参数 18
3.7.3 按弯强度曲初算模数m 21
3.7.4 齿轮疲劳强度校核 23
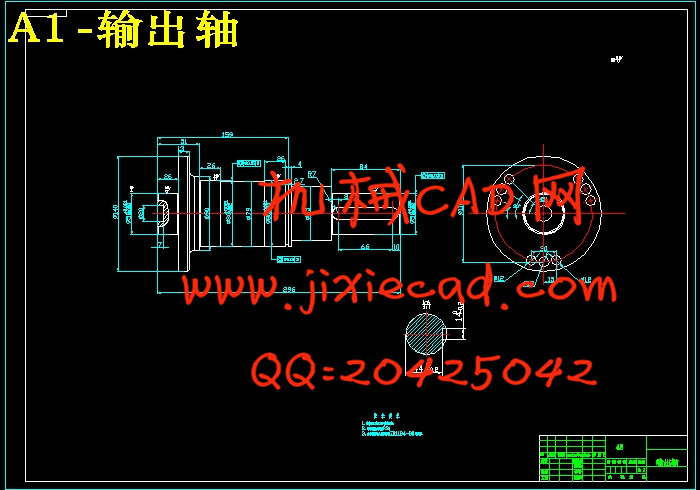
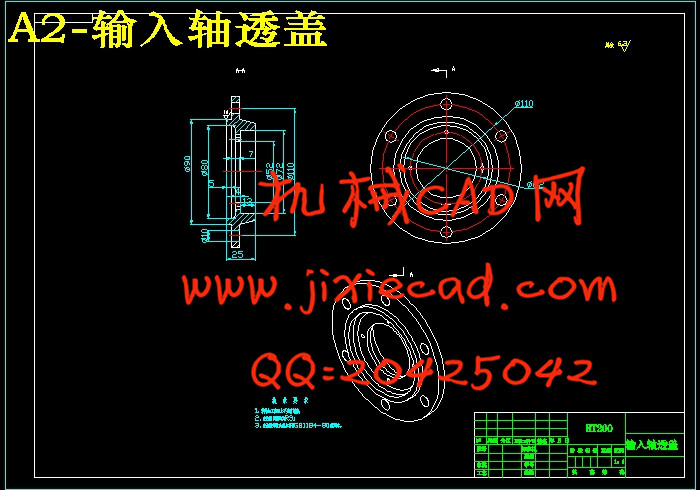
3.8 轴上部件的设计计算与校核 28
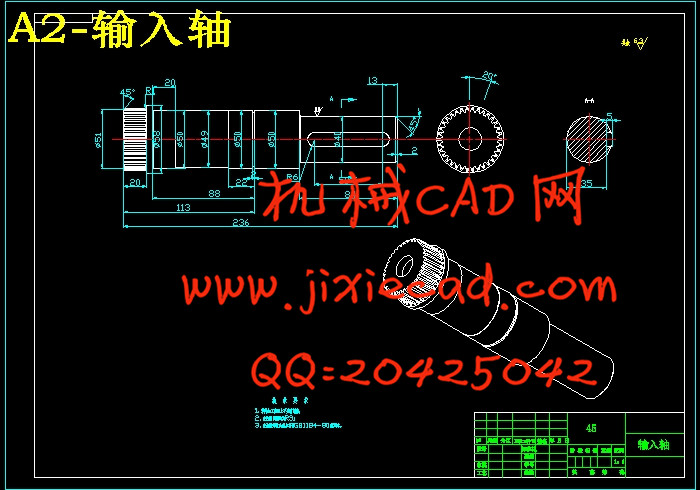
3.8.1 轴的计算 28
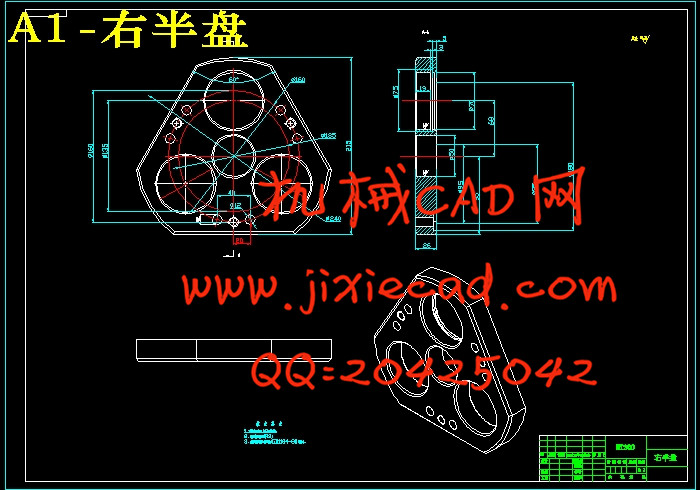
3.8.2 行星架设计 34
3.9 键的选择与校核 38
3.9.1 键的选择 38
3.9.2 键的校核 38
3.10 联轴器的选择 40
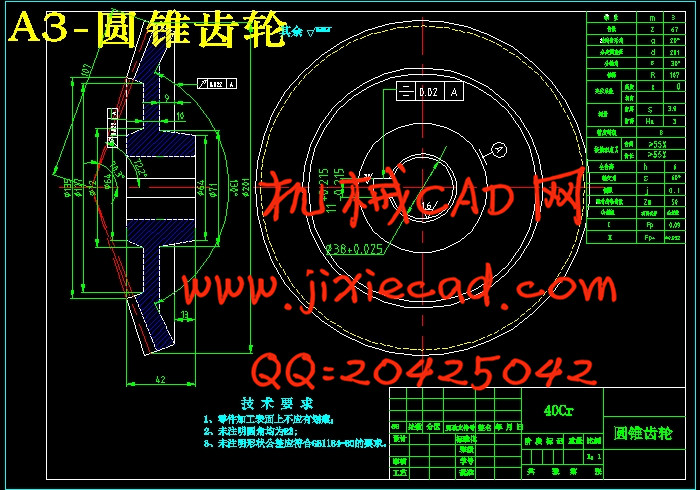
第4章 圆锥直齿轮设计 41
4.1 选定齿轮精度等级、材料及齿数 41
4.2 轴的设计计算 45
4.3 滚动轴承的选择及计算 50
总 结 52
参考文献 53
致 谢 54