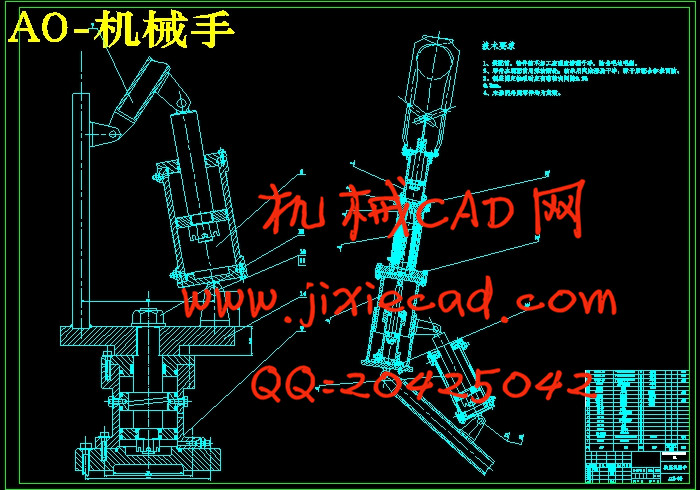
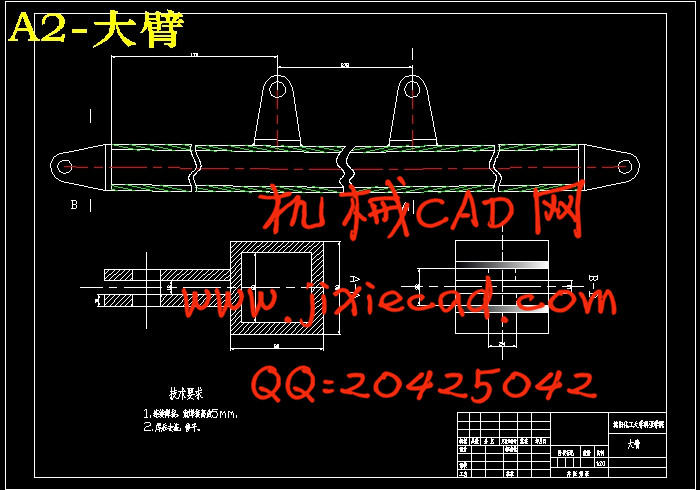
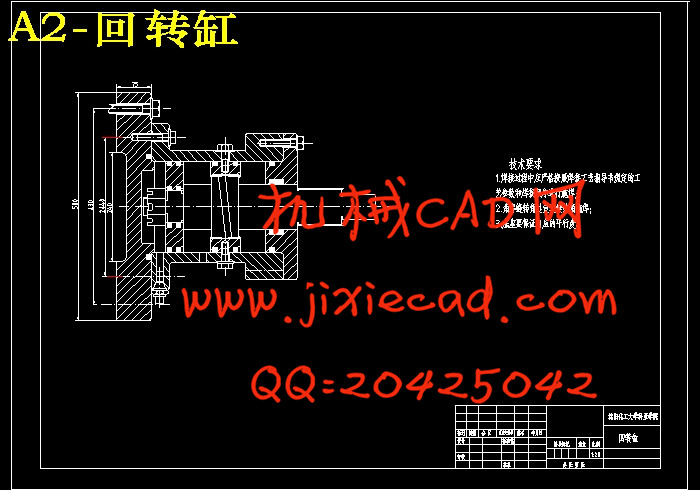
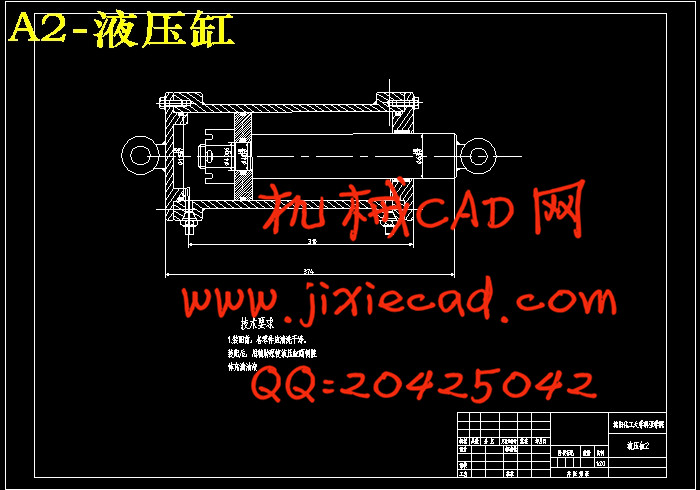
设计简介
摘要
1998年ABB公司推出IRbl400系列小机器人,其循环时间只有0.4s,控制器包括软件、高压电、驱动器、用户接口等皆集成于一柜,只有洗衣机变换器那样大小。FANUC公司2000年9月宣称它的控制器为世界最小。工业机器人的应用从单机、单元向系统发展。多达百台以上的机器人群与微机及周边智能设备和操作人员形成一个大群体(多智能体)。跨国大集团的垄断和全球化的生产将世界众多厂家的产品联接在一起,实现了标准化、开放化、网络化的“虚拟制造”,为工业机器人系统化的发展推波助澜。机器人技术是涉及机械学、传感器技术、驱动技术、控制技术、通信技术和计算机技术的一门综合性高新技术,既是光机电软一体化的重要基础,又是光机电软一体化技术的典型代表。其产品主要有两大类,即以日本和瑞典为代表的一系列特定应用的机器人,如弧焊、点焊、喷漆装备、刷胶和建筑等,并形成了庞大的机器人产业。
另一类是以美国、英国为代表的智能机器人开发,由于人工智能和其它智能技术的发展远落后于人们对它的期望,目前绝大部分研究成果未能走出实验室。机器人系统集成技术也是由几个主要发达国家所垄断。近年来,机器人技术并未出现突破性进展,各国的机器人技术研究机构和制造厂商都继续在技术深化、引进新技术和扩大应用领域等方面进行探索。
关键词: 机械手; 液压缸; 液压传动; 活塞
Abstract
1998 ABB IRbl400 series small robot, the cycle time of only 0.4 s, controller including software, high voltage, drive, and user interface are integrated in a cabinet, only washing machine size converter. FANUC company in September 2000 claimed its controller is the smallest. The application of industrial robots from single machine, the unit to the system development. Up to more than one hundred sets of machines of microcomputer and people in and around intelligent equipment and operating personnel to form a large group (multi-agent). Multinational conglomerates of monopoly and the globalization of the world many manufacturers products join together, has realized the standardization, open, networked \"virtual manufacturing", for the development of the industrial robot systematic. Robotics is related to mechanics, sensor technology, drive technology, control technology, communication technology and computer technology of a comprehensive new and high technology, is not only the important opto-mechatronics integration of soft foundation, a typical representative of the soft and optical integration technology. Its products mainly include two categories, namely, represented by Japan and Sweden, a series of specific application of the robot, such as arc welding, spot welding, spray painting equipment, cementing and construction, etc., and formed a huge industry robot.
Another kind is the intelligent robot development represented by the United States, Britain, due to the development of artificial intelligence and other intelligence is far behind the people expect of it, at present most of the results of the study are not out of the lab. Robot system integration technology is dominated by several major developed countries. There was no breakthrough in recent years, robot technology, robot technology research institutions and manufacturers of all countries are to continue deepening in technology, the introduction of new technology to explore and expand the application field, etc.
Key words: Manipulator; Hydraulic Cylinder; Hydraulic Drive; Piston
目 录1998年ABB公司推出IRbl400系列小机器人,其循环时间只有0.4s,控制器包括软件、高压电、驱动器、用户接口等皆集成于一柜,只有洗衣机变换器那样大小。FANUC公司2000年9月宣称它的控制器为世界最小。工业机器人的应用从单机、单元向系统发展。多达百台以上的机器人群与微机及周边智能设备和操作人员形成一个大群体(多智能体)。跨国大集团的垄断和全球化的生产将世界众多厂家的产品联接在一起,实现了标准化、开放化、网络化的“虚拟制造”,为工业机器人系统化的发展推波助澜。机器人技术是涉及机械学、传感器技术、驱动技术、控制技术、通信技术和计算机技术的一门综合性高新技术,既是光机电软一体化的重要基础,又是光机电软一体化技术的典型代表。其产品主要有两大类,即以日本和瑞典为代表的一系列特定应用的机器人,如弧焊、点焊、喷漆装备、刷胶和建筑等,并形成了庞大的机器人产业。
另一类是以美国、英国为代表的智能机器人开发,由于人工智能和其它智能技术的发展远落后于人们对它的期望,目前绝大部分研究成果未能走出实验室。机器人系统集成技术也是由几个主要发达国家所垄断。近年来,机器人技术并未出现突破性进展,各国的机器人技术研究机构和制造厂商都继续在技术深化、引进新技术和扩大应用领域等方面进行探索。
关键词: 机械手; 液压缸; 液压传动; 活塞
Abstract
1998 ABB IRbl400 series small robot, the cycle time of only 0.4 s, controller including software, high voltage, drive, and user interface are integrated in a cabinet, only washing machine size converter. FANUC company in September 2000 claimed its controller is the smallest. The application of industrial robots from single machine, the unit to the system development. Up to more than one hundred sets of machines of microcomputer and people in and around intelligent equipment and operating personnel to form a large group (multi-agent). Multinational conglomerates of monopoly and the globalization of the world many manufacturers products join together, has realized the standardization, open, networked \"virtual manufacturing", for the development of the industrial robot systematic. Robotics is related to mechanics, sensor technology, drive technology, control technology, communication technology and computer technology of a comprehensive new and high technology, is not only the important opto-mechatronics integration of soft foundation, a typical representative of the soft and optical integration technology. Its products mainly include two categories, namely, represented by Japan and Sweden, a series of specific application of the robot, such as arc welding, spot welding, spray painting equipment, cementing and construction, etc., and formed a huge industry robot.
Another kind is the intelligent robot development represented by the United States, Britain, due to the development of artificial intelligence and other intelligence is far behind the people expect of it, at present most of the results of the study are not out of the lab. Robot system integration technology is dominated by several major developed countries. There was no breakthrough in recent years, robot technology, robot technology research institutions and manufacturers of all countries are to continue deepening in technology, the introduction of new technology to explore and expand the application field, etc.
Key words: Manipulator; Hydraulic Cylinder; Hydraulic Drive; Piston
第一章绪论 1
第二章手部结构设计 2
2.1 手抓的结构选定 2
2.2 液压缸的选定 3
2.2.1 液压缸内径的确定 3
2.2.2液压缸外径的确定 3
2.2.4 液压缸活塞杆的确定及校核 4
2.2.5 活塞的最大行程 4
2.2.6钢筒底部厚度的确定 4
2.2.7 缸盖螺钉的计算 5
2.2.8 钢筒头部法兰厚度的确定 6
2.2.9 液压缸其它元件的确定 7
第三章摆动缸的选定 8
3.1 联接部分的设计 8
3.2 连接部分材料的选定与连接方法 9
第四章手臂的结构设计 10
4.1 手臂的结构初定 10
4.2 小臂受力分析 10
4.3 小臂液压缸的确定 11
4.3.1 小臂液压缸的受力分析 11
4.3.2 液压缸内径的确定 11
4.3.3 液压缸外径的确定 11
4.3.4 钢筒壁厚校核 12
4.3.5 液压缸活塞杆的确定及校核 13
4.3.6 活塞的最大行程 13
4.3.7 钢筒底部厚度的确定 13
4.3.8 缸盖螺钉的计算 14
4.3.9 钢筒头部法兰厚度的确定 15
4.3.10 液压缸其它元件的确定 16
4.4 小臂套筒的设计 17
4.4.1 材料的选定 17
4.4.2 内套的设计 17
4.4.3 外套的设计 17
第五章支小臂液压缸的确定 18
5.1 支小臂液压缸的摆动角度确定 18
5.2 支小臂缸的受力分析 18
5.3 液压缸的确定 19
5.3.1 液压缸内径的确定 19
5.3.2 液压缸的外径及壁厚的确定 19
5.3.3 液压缸活塞杆的确定及校核 20
5.3.4 活塞的最大行程 21
5.3.5 钢筒底部厚度的确定 21
5.3.6 缸盖螺钉的计算 22
5.3.7 缸盖头部法兰厚度的确定 23
5.3.8 缸筒与端部焊接 24
5.3.9 液压缸的其他元件的确定 24
第六章大臂的结构设计 26
6.1 大臂材料的选定 26
6.2 大臂受力受力分析 26
6.3 支大臂液压缸的确定 27
6.3.1 液压缸内径的确定 27
6.3.2 液压缸的外径及壁厚的确定 28
6.3.3 缸筒壁厚的校核 28
6.3.4 液压缸活塞杆的确定及校核 29
6.3.5 活塞杆的最大允许行程 29
6.3.6钢筒底部厚度的确定 30
6.3.7 缸盖螺钉的计算 30
6.3.8 缸盖头部法兰厚度的确定 32
6.3.9 缸筒与端部焊接 32
6.3.10 液压缸的其他元件的确定 33
第七章底座的设计 34
7.1 底座材料及尺寸选定 34
7.2 底板螺栓的确定 34
7.2.1 受翻转力矩的螺栓组连接 34
7.2.2 缸盖螺钉的计算 35
第八章液压系统传动方案的确定 36
8.1 各液压缸的换向回路 36
8.2 调速方案 36
第九章计算和选择液压元件 37
9.1 阀的种类和功用 37
9.2 拟定液压系统 37
9.3 液压系统中的辅助装置 38
第十章液压系统原理图 38
结论 41
参考文献 42
致谢 43