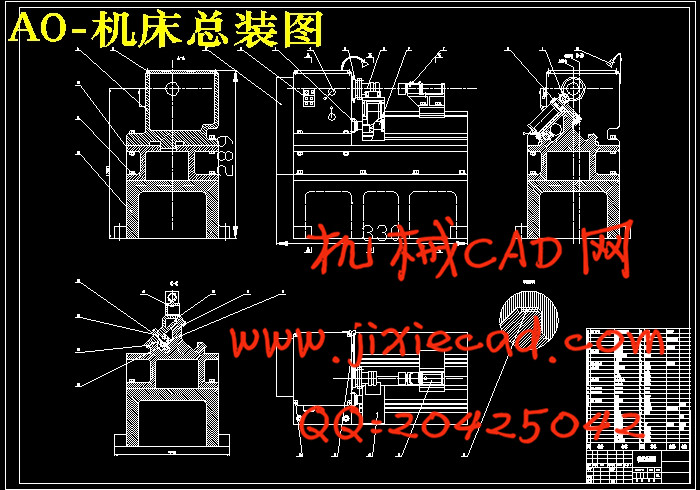
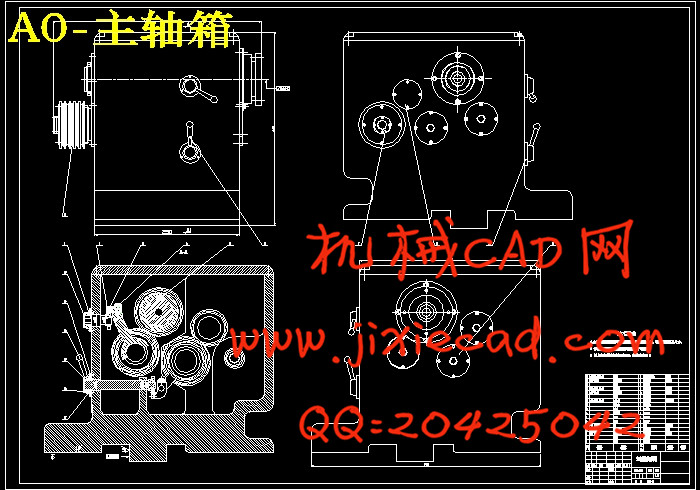
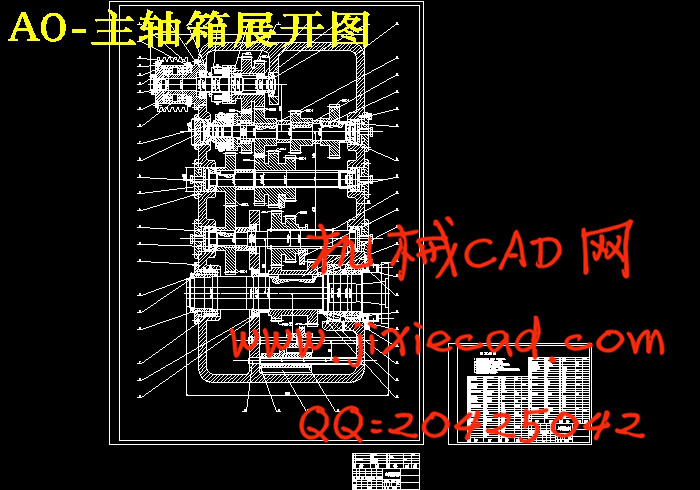
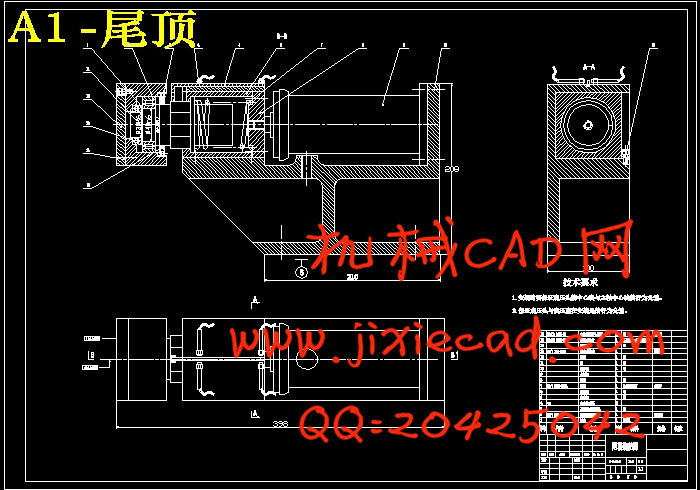
设计简介
摘 要
随着,各项技术的发展,机械技术、电子技术、液压技术的互相渗透越来越多,越来越快。机电液有机的结合是实现机电业一体化的短小、轻、薄、和智能化。本设计的特点是,以机械为主、以液压为动力部分。此次毕业设计根据学校和老师的要求要运用机械、电子、及液压等多方面知识来完成,机电液一体化。机电液一体化是机械工业的发展方向,是机械与微电子以及液压技术的新型交叉科学。所谓一体化“一体化”并不是机械技术电子技术和液压技术的简单组合。而是互相取长补短、有机结合,以实现系统构成的最佳化。
毕业设计是大学学习的最后一个教学环节,全国高教机械设计及制造专业教学指导委员会第三次会议记要指出,“毕业设计题目应该以产品(或工程)设计类题目为主,尤其要鼓励去工厂从高真实产品设计”。在实际工程设计中,学生可以得到所学过的理论基础,技术基础,专业课全面的训练,为将来做好机械设计工程师的工作,提供全面的锻炼机会。
关键词:主轴箱、旋压、尾顶、传感器、PLC。
ABSTRACT
Along with the, the technical development, the mechanical technology, electronic technology, hydraulic technology mutual penetration is more and more, more and more quickly. Mechanical and electronic liquid organic combination is to realize the integration of the JiDianYe short, light, thin, and smart. This design characteristic is to mechanical primarily, hydraulic power for parts.
The graduation design according to the requirements of the school and the teachers to use machinery, electronics, and hydraulic and so on various knowledge to complete, and mechanical and electrical integration of liquid. Mechanical and electrical integration is the liquid the development direction of mechanical industry, is the mechanical and microelectronics and hydraulic technology of the new interdisciplinary science. The integration of so-called "integration" is not mechanical technology and electronic technology and hydraulic technology simple combination. But from each other, combined organically, so as to realize the system structure optimization.
Graduation design is the last of a university to study the teaching link, the national higher education mechanical design and manufacturing professional education committee third meeting minutes points out, "the graduation design topic should product (or engineering) design kind of topic primarily, especially to encourage to factories from high real product design". In the practical engineering design, students can get the learned the theoretical basis, and technology base, professional class comprehensive training for the future to the mechanical design engineer work, to provide comprehensive training opportunities.
Keywords: Spindle Box Spinning Tail Top Sensors PLC
目 录
绪 论…………………………………………………………………………………………………………1
第1 章 旋压机床的总体设计……………………………………………………………………………2
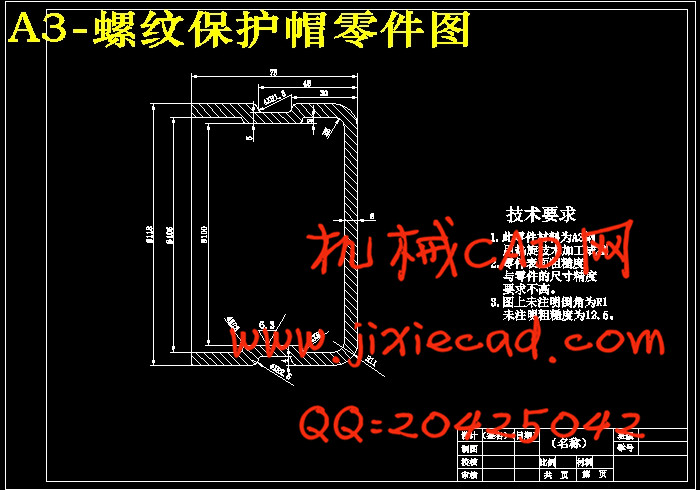
1.1被加工零件方案设计分析旋压设备概述………………………………………………………2
1.2 旋压设备概述…………………………………………………………………………………2
1.3旋压机床设计应满足的基本要求…………………………………………………………………2
1.4 旋压机床设计步骤 ………………………………………………………………………………3
1.5 旋压机床的总体布局 ………………………………………………………………………4
第2 章 轴的设计与计算 ……………………………………………………………………………5
2.1主轴参数的选择与计算………………………………………………………………5
2.2 选择轴的材料并确定许用应力………………………………………………………………6
2.2 主轴的校核……………………………………………………………………………………7
第3 章 传动设计……………………………………………………………………………………8
3.1 主传动系设计………………………………………………………………………………8
3.1.1主轴转速的确定………………………………………………………………………8
3.1.2公比Φ,变速范围Rn和级数Z的确定………………………………………………8
3.1.3 选择结构式……………………………………………………………………………8
3.1.4 确定是否需要增加降速定比传动副 ………………………………………………………8
3.1.5分配各变速组的最小传动比,拟订转速图……………………………………………8
3.1.6齿轮齿数的确定………………………………………………………………………9
3.2 带传动设计…………………………………………………………………………………10
3.3 摩擦式电磁离合器布置……………………………………………………………………11
3.4 直齿圆柱齿轮齿根弯曲疲劳强度计算……………………………………………………12
3.4.1 名义载荷……………………………………………………………………………12
3.4.2 计算载荷……………………………………………………………………………12
3.4.3 直齿圆柱齿轮受力分析……………………………………………………………13
Ⅰ
3.4.4 直齿圆柱齿轮齿根弯曲疲劳强度计算……………………………………………14
第4 章 进给机构设计………………………………………………………………………………15
4.1 旋轮座………………………………………………………………………………………15
4.2旋压力的计算 ………………………………………………………………………………16
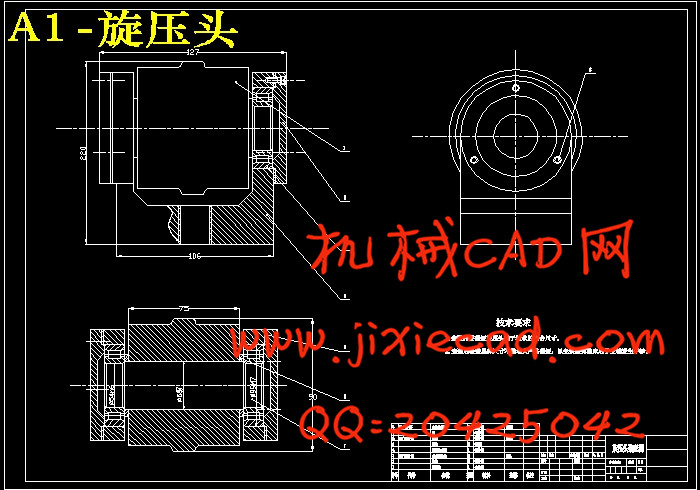
4.3旋压头 ………………………………………………………………………………………16
第5章 尾顶的设计…………………………………………………………………………………17
5.1 尾座的要求…………………………………………………………………………………17
5.2 尾顶力的计算………………………………………………………………………………17
5.3 尾顶的结构设计……………………………………………………………………………18
第6章 支撑部件导轨的设计………………………………………………………………………19
6.1 设计原则……………………………………………………………………………………19
6.2 床身的设计…………………………………………………………………………………19
6.3 导轨的结构设计…………………………………………………………………………20
6.4 导轨材料与热处理………………………………………………………………………20
6.5 导轨的技术要求 …………………………………………………………………………21
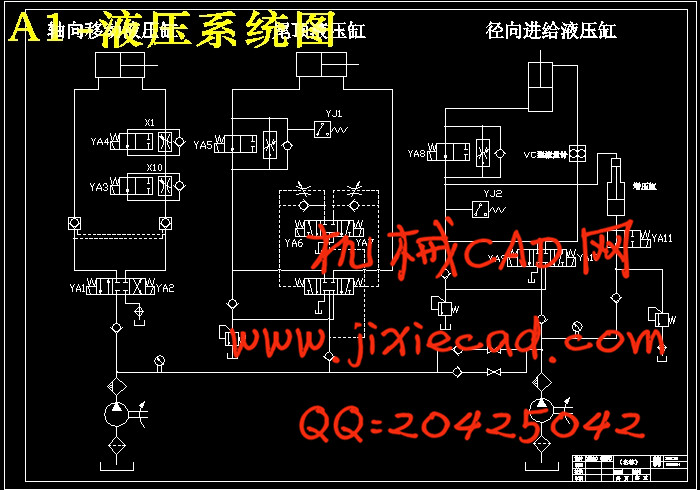
第7章 液压系统的设计计算 ………………………………………………………………………22
7.1 液压力的计算 ………………………………………………………………………………22
7.2 验算液压系统性能 ………………………………………………………………………23
第8章 机床电路设计………………………………………………………………………………25
8.1 电气控制部件介绍… ………………………………………………………………………26
8.2 控制过程分析和设备的选用………………………………………………………27
8.3 PLC编程……………………………………………………………………………………28
结 论……………………………………………………………………………………………………30
致 谢……………………………………………………………………………………………………31
参考文献 …………………………………………………………………………………………………32