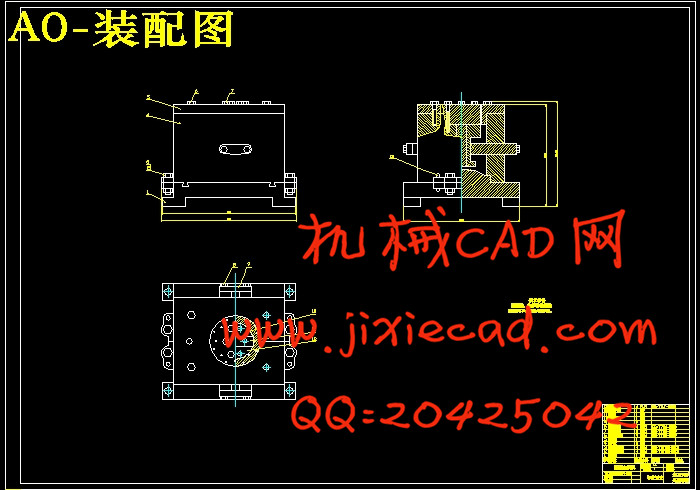
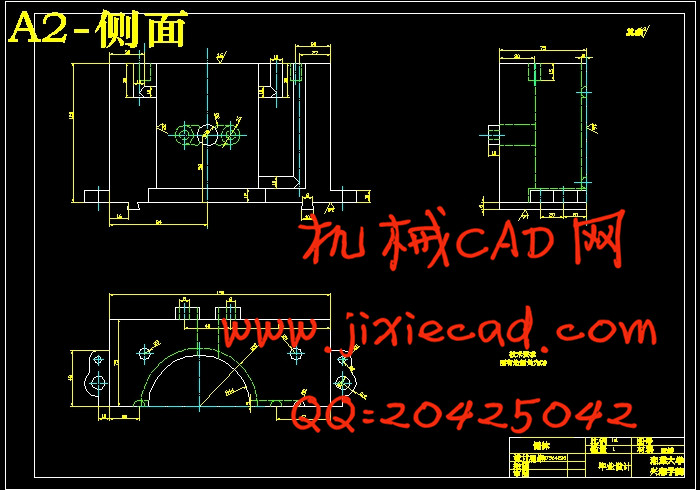
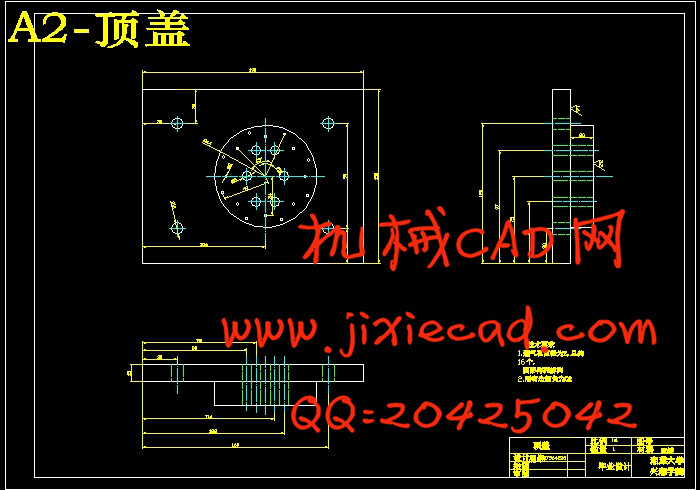
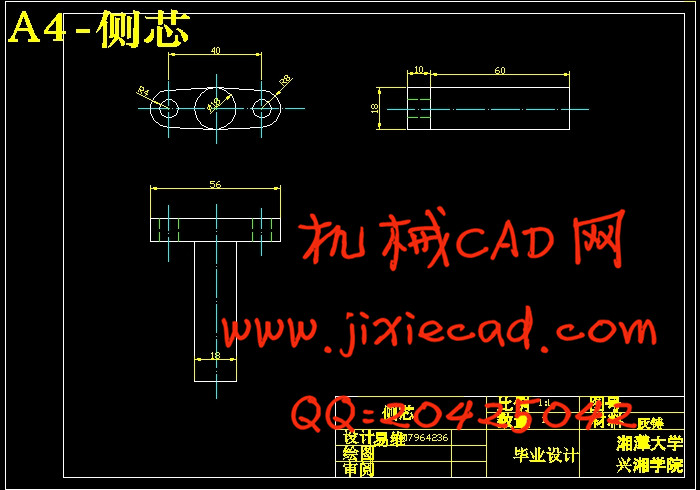
设计简介
摘要
汽车发动机的活塞是发动机中的主要配件之一,它与活塞环、活塞销等零件组成活塞组,与气缸盖等共同组成燃烧室,承受燃气作用力并通过活塞销和连杆把动力传给曲轴,以完成内燃发动机的工作过程。油气燃烧所产生的热由活塞的顶部所吸收,并传至气缸壁,而燃烧后气体膨胀所产生的力量也必须经由活塞来吸收,活塞会把燃烧气体压力及惯性力经由连杆传到曲轴上,利用连杆的作用将活塞的线性往复运动转换曲轴的旋转运动。
活塞的功用是承受气体压力,井通过活塞销传给连杆驱使曲轴旋转,活塞项部还是燃烧室的组成部分。活塞在高温、高压、高速、润滑不良的条件下1二作。活塞在气缸内以很高的速度往复运动,且速度在不断地变化,这就产生了很大的惯性力,使活塞受到很大的附加载荷。活塞在这种恶劣的条件’卜工作,会产生变形并加速磨损,还会产生附加载荷和热应力,同时受到燃气的化学腐蚀作用。现代的活塞设计主要有铸造和锻造两种,而铸造又比锻造简单便宜,但却不及锻造活塞能承受较大的热度和压力。由于活塞与活塞环都必须在高温、高压、高速及临界润滑的状态’卜工作,因此长期以来,发动机设计者都为提供一个最佳的设计而不断努力,进而可以从活塞方而来提高引擎的性能。
本文以捷达EA113汽油机的相关参数作为参考,对四缸汽油机的曲柄连杆机构的主要零部件进行了结构设计计算,并对曲柄连杆机构进行了有关运动学和动力学的理论分析与计算机仿真分析。
首先,以运动学和动力学的理论知识为依据,对曲柄连杆机构的运动规律以及在运动中的受力等问题进行详尽的分析,并得到了精确的分析结果。其次分别对活塞组、连杆组以及曲轴进行详细的结构设计,并进行了结构强度和刚度的校核。一再次,应用三维CAD软件:Pro/Engineer建立了曲柄连杆机构各零部件的几何模型,在此工作的基础上,利用Pro/E软件的装配功能,将曲柄连杆机构的各组成零件装配成活塞组件、连杆组件和曲轴组件,然后利用Pro/E软件的机构分析模块(Pro/Mechanism),建立曲柄连杆机构的多刚体动力学模型,进行运动学分析和动力学分析模拟,研究了在不考虑外力作用并使曲轴保持匀速转动的情况下,活塞和连杆的运动规律以及曲柄连杆机构的运动包络。仿真结果的分析表明,仿真结果与发动机的实际工作状况基木一致,文章介绍的仿真方法为活塞组的结构,优化设计提供了一种新思路。
关键词: 活塞 气缸盖 燃烧室 曲轴 惯性力 附加载荷
ABSTRACT
The piston of car motor is one of the main accessorieses in the motor ,it and the piston wreath ,piston sell etc .the spare parts constitute a piston set and cover with air cylinder etc. Constitute combustion room together , bear gas function the dint also sell through a piston and connect the pole motive song stalk to complete inside the work process of ran motor.the oil annoys the combustion produce of hot from the coping of piston absorb , and spread to air cylinder wall , and combustion empress thestrengh produced by air inflation have to also absorb through the piston , the piston will chase combustion air pressure and inertial dint through connect the spread to song stalk up , make use of connect the function of pole exercise the line back and forth of piston to convert revolving of song stalk sport.
The effect of piston bears air pressure , and sell to pass to connect a pole to order about song stalk to revolve through a piston , constituting of the piston a coping still a combustion room part .piston under the condition that heat ,high pressure , high speed , lubricate bad work . The piston is exercised with very high speed back and forth in the air cylinder , and speed at constantly variety , this produced very greatly inertial inertial dint and made the piston been subjected to very big of the affixture carry a lotus . The piston is under this bad condition work , will produce to transform and accelerate to wear away , also produce affixture to carry lotus and heat in response to the dint , be subjected to chemistry of the gas corrosion function in the meantime . Modern of the piston design to mainly have the foundry forging 2 kinds , but cast again than forging simple cheapness , but cannot compare with forging piston can bear bigger heat and pressure . Piston and piston wreaths have to work under the appearance of the heat , high pressure and high speed and the critical lubrication , therefore for long time , the motor designs all continuously make great effort for providing a design , then can raise the function of from the piston .
目录
摘要····································································································1
ABSTRACT·······················································································2
第一章 活塞的运行原理和工作条件················································3
2.1 活塞的运行原理········································································3
2.2 活塞的机械负荷········································································3
2.3 活塞的热负荷···········································································3
2.4 磨损强烈··················································································3
第二章 汽油机结构参数得选取·······················································4
1.1 汽缸直径的确定········································································4
1.2 转速n的确定···········································································4
1.3 汽缸工作容积与升功率·······························································4
1.4 缸心距的确定············································································5
1.5 压缩比与燃烧室容积Vc,总容积Va············································5
第三章 活塞组的设计·······································································6
3.1 活塞组的设计要求·····································································6
3.2 活塞的材料···············································································6
3.3 活塞各部分尺寸·········································································7
3.4 活塞总尺寸············································································13
第四章 活塞加工············································································15
第五章 活塞铸造方式的选取及优缺点··········································16
5.1 铸造方式的比较······································································16
5.2 铝合金的铸造方式的选取及优缺点···········································17
第六章 金属型的设计·····································································18
6.1 冒口的设计·············································································18
6.2 浇注系统的设计·······································································20
6.3 金属型的设计··········································································21
6.4 金属型芯的设计·····································································26
总结··································································································28
参考文献···························································································29
汽车发动机的活塞是发动机中的主要配件之一,它与活塞环、活塞销等零件组成活塞组,与气缸盖等共同组成燃烧室,承受燃气作用力并通过活塞销和连杆把动力传给曲轴,以完成内燃发动机的工作过程。油气燃烧所产生的热由活塞的顶部所吸收,并传至气缸壁,而燃烧后气体膨胀所产生的力量也必须经由活塞来吸收,活塞会把燃烧气体压力及惯性力经由连杆传到曲轴上,利用连杆的作用将活塞的线性往复运动转换曲轴的旋转运动。
活塞的功用是承受气体压力,井通过活塞销传给连杆驱使曲轴旋转,活塞项部还是燃烧室的组成部分。活塞在高温、高压、高速、润滑不良的条件下1二作。活塞在气缸内以很高的速度往复运动,且速度在不断地变化,这就产生了很大的惯性力,使活塞受到很大的附加载荷。活塞在这种恶劣的条件’卜工作,会产生变形并加速磨损,还会产生附加载荷和热应力,同时受到燃气的化学腐蚀作用。现代的活塞设计主要有铸造和锻造两种,而铸造又比锻造简单便宜,但却不及锻造活塞能承受较大的热度和压力。由于活塞与活塞环都必须在高温、高压、高速及临界润滑的状态’卜工作,因此长期以来,发动机设计者都为提供一个最佳的设计而不断努力,进而可以从活塞方而来提高引擎的性能。
本文以捷达EA113汽油机的相关参数作为参考,对四缸汽油机的曲柄连杆机构的主要零部件进行了结构设计计算,并对曲柄连杆机构进行了有关运动学和动力学的理论分析与计算机仿真分析。
首先,以运动学和动力学的理论知识为依据,对曲柄连杆机构的运动规律以及在运动中的受力等问题进行详尽的分析,并得到了精确的分析结果。其次分别对活塞组、连杆组以及曲轴进行详细的结构设计,并进行了结构强度和刚度的校核。一再次,应用三维CAD软件:Pro/Engineer建立了曲柄连杆机构各零部件的几何模型,在此工作的基础上,利用Pro/E软件的装配功能,将曲柄连杆机构的各组成零件装配成活塞组件、连杆组件和曲轴组件,然后利用Pro/E软件的机构分析模块(Pro/Mechanism),建立曲柄连杆机构的多刚体动力学模型,进行运动学分析和动力学分析模拟,研究了在不考虑外力作用并使曲轴保持匀速转动的情况下,活塞和连杆的运动规律以及曲柄连杆机构的运动包络。仿真结果的分析表明,仿真结果与发动机的实际工作状况基木一致,文章介绍的仿真方法为活塞组的结构,优化设计提供了一种新思路。
关键词: 活塞 气缸盖 燃烧室 曲轴 惯性力 附加载荷
ABSTRACT
The piston of car motor is one of the main accessorieses in the motor ,it and the piston wreath ,piston sell etc .the spare parts constitute a piston set and cover with air cylinder etc. Constitute combustion room together , bear gas function the dint also sell through a piston and connect the pole motive song stalk to complete inside the work process of ran motor.the oil annoys the combustion produce of hot from the coping of piston absorb , and spread to air cylinder wall , and combustion empress thestrengh produced by air inflation have to also absorb through the piston , the piston will chase combustion air pressure and inertial dint through connect the spread to song stalk up , make use of connect the function of pole exercise the line back and forth of piston to convert revolving of song stalk sport.
The effect of piston bears air pressure , and sell to pass to connect a pole to order about song stalk to revolve through a piston , constituting of the piston a coping still a combustion room part .piston under the condition that heat ,high pressure , high speed , lubricate bad work . The piston is exercised with very high speed back and forth in the air cylinder , and speed at constantly variety , this produced very greatly inertial inertial dint and made the piston been subjected to very big of the affixture carry a lotus . The piston is under this bad condition work , will produce to transform and accelerate to wear away , also produce affixture to carry lotus and heat in response to the dint , be subjected to chemistry of the gas corrosion function in the meantime . Modern of the piston design to mainly have the foundry forging 2 kinds , but cast again than forging simple cheapness , but cannot compare with forging piston can bear bigger heat and pressure . Piston and piston wreaths have to work under the appearance of the heat , high pressure and high speed and the critical lubrication , therefore for long time , the motor designs all continuously make great effort for providing a design , then can raise the function of from the piston .
目录
摘要····································································································1
ABSTRACT·······················································································2
第一章 活塞的运行原理和工作条件················································3
2.1 活塞的运行原理········································································3
2.2 活塞的机械负荷········································································3
2.3 活塞的热负荷···········································································3
2.4 磨损强烈··················································································3
第二章 汽油机结构参数得选取·······················································4
1.1 汽缸直径的确定········································································4
1.2 转速n的确定···········································································4
1.3 汽缸工作容积与升功率·······························································4
1.4 缸心距的确定············································································5
1.5 压缩比与燃烧室容积Vc,总容积Va············································5
第三章 活塞组的设计·······································································6
3.1 活塞组的设计要求·····································································6
3.2 活塞的材料···············································································6
3.3 活塞各部分尺寸·········································································7
3.4 活塞总尺寸············································································13
第四章 活塞加工············································································15
第五章 活塞铸造方式的选取及优缺点··········································16
5.1 铸造方式的比较······································································16
5.2 铝合金的铸造方式的选取及优缺点···········································17
第六章 金属型的设计·····································································18
6.1 冒口的设计·············································································18
6.2 浇注系统的设计·······································································20
6.3 金属型的设计··········································································21
6.4 金属型芯的设计·····································································26
总结··································································································28
参考文献···························································································29