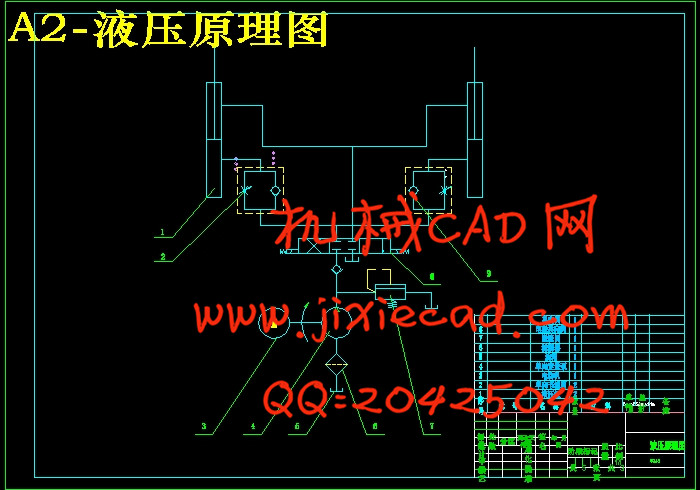
设计简介
摘 要:近年来,随着人民生活水平的不断提高,越来越多的人购买了私家车。数量众多的汽车停放,对城市的交通和环境起着重大的影响。而停车难问题的出现,也给机械停车设备行业带来了巨大的商机和广阔的市场。
由于很多新建小区内住户与车位的配比为1:1,为了解决停车位占地面积与住户商用面积的矛盾,立体停车设备以其平均单车占地面积小的独特特性,已被广大用户接受。
在此设计中,通过利用杠杆和链传动曳引活动梁实现对汽车的二层存取。
在完成确保双层车辆均可自由存取的总体框架的设计后,对链传动存取车辆装置及其零部件、活动梁及停车梁等主要结构及其零部件进行计算校核。
该立体车库结构简单,操作方便,成本低廉,比较适合于家庭用户。
关键词:立体车库;杠杆;链传动; 曳引 ;校核
Abstract:In recent years, with the continuous improvement of people's living standards, more and more people buy private cars. The number of cars parked plays a significant impact on the city's traffic and the environment. Parking difficult problems arise, but also to the mechanical parking equipment industry has brought great business opportunities and a broad market.
Residents parking spaces in a lot of new residential ratio of 1:1, in order to solve the contradiction between the commercial area of the parking space covers an area of household, parking equipment its average cycle small footprint unique characteristics, has been the majority of users accept .
In this design, achieved through the use of leverage and chain drive traction of the beams to access the second floor of the car.
Completed to ensure that the design of the overall framework of double vehicles are free to access, access to vehicles, chain drive device and its components, the beams and parking beam structure and its components are calculated check.
The three-dimensional garage is simple in structure, easy to operate, low cost, more suitable for home users.
Key words: Stereoscopic Garage; Level; Transportation of Chain; Tractor-driven; Check
3 主要部件强度刚度校核……………………………………………………………17
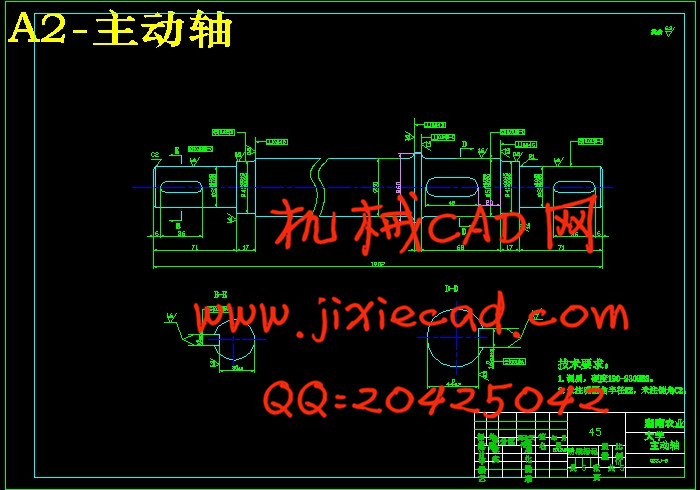
3.1.1主动轴的强度校核……………………………………………………………17
3.1.2主动轴的刚度校核……………………………………………………………19
3.1.3从动轴的强度校核……………………………………………………………21
3.1.4从动轴的刚度校核……………………………………………………………25
3.2轴承和键的校核…………………………………………………………………27
3.2.1轴承的校核……………………………………………………………………27
3.2.2键的强度校核…………………………………………………………………28
3.3梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………………29
3.3.1梁的自由扭转计算……………………………………………………………29
3.3.2活动梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………30
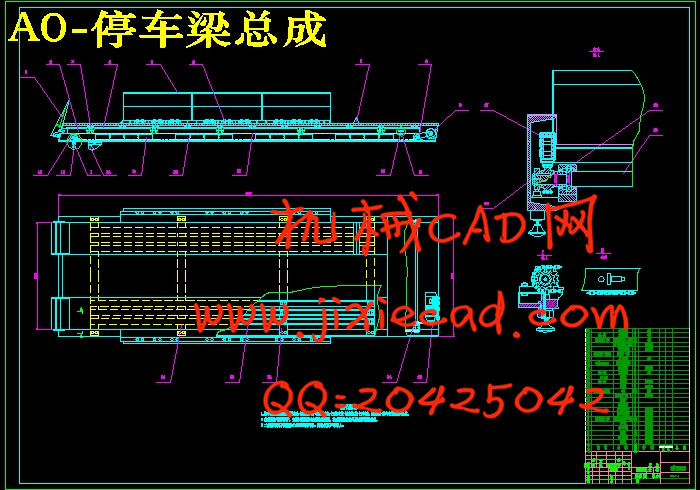
3.3.3停车梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………36
3.4本章小结…………………………………………………………………………40
结束语…………………………………………………………………………………40
参考文献………………………………………………………………………………40
致谢 ……………………………………………………………………………………41
由于很多新建小区内住户与车位的配比为1:1,为了解决停车位占地面积与住户商用面积的矛盾,立体停车设备以其平均单车占地面积小的独特特性,已被广大用户接受。
在此设计中,通过利用杠杆和链传动曳引活动梁实现对汽车的二层存取。
在完成确保双层车辆均可自由存取的总体框架的设计后,对链传动存取车辆装置及其零部件、活动梁及停车梁等主要结构及其零部件进行计算校核。
该立体车库结构简单,操作方便,成本低廉,比较适合于家庭用户。
关键词:立体车库;杠杆;链传动; 曳引 ;校核
Abstract:In recent years, with the continuous improvement of people's living standards, more and more people buy private cars. The number of cars parked plays a significant impact on the city's traffic and the environment. Parking difficult problems arise, but also to the mechanical parking equipment industry has brought great business opportunities and a broad market.
Residents parking spaces in a lot of new residential ratio of 1:1, in order to solve the contradiction between the commercial area of the parking space covers an area of household, parking equipment its average cycle small footprint unique characteristics, has been the majority of users accept .
In this design, achieved through the use of leverage and chain drive traction of the beams to access the second floor of the car.
Completed to ensure that the design of the overall framework of double vehicles are free to access, access to vehicles, chain drive device and its components, the beams and parking beam structure and its components are calculated check.
The three-dimensional garage is simple in structure, easy to operate, low cost, more suitable for home users.
Key words: Stereoscopic Garage; Level; Transportation of Chain; Tractor-driven; Check
目 录
摘要……………………………………………………………………………………1
关键词…………………………………………………………………………………1
1前言…………………………………………………………………………………2
1.1课题背景…………………………………………………………………………2
1.2 国外研究现状 ……………………………………………………………………3
1.3 国内研究现状……………………………………………………………………4
1.4 主要研究内容……………………………………………………………………4
2 方案选择及结构设计……………………………………………………………… 5
2.1立体车库总体结构设计…………………………………………………………5
2.1.1车型及车库参数………………………………………………………………5
2.1.2 车库工作流程…………………………………………………………………5
2.2 液压系统部件的选择与计算……………………………………………………5
2.2.1液压缸的选择与计算…………………………………………………………5
2.2.2液压泵的选择…………………………………………………………………8
2.2.3泵电动机的选择………………………………………………………………9
2.3传动部件的选择与计算…………………………………………………………10
2.3.1减速机的选择…………………………………………………………………10
2.3.2链条的设计……………………………………………………………………10
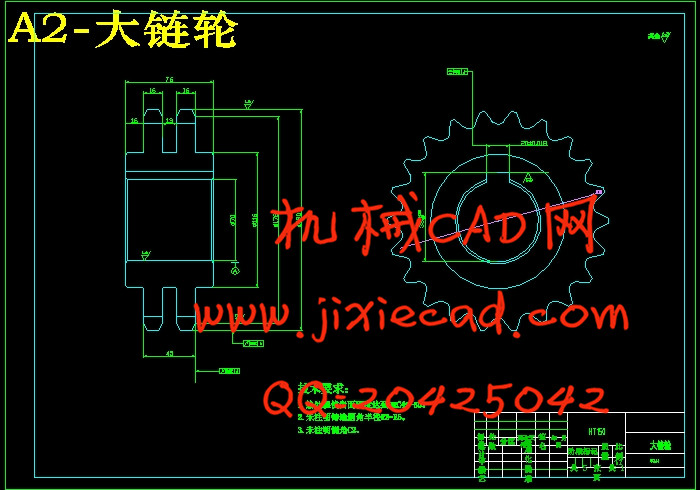
2.3.3链轮的设计……………………………………………………………………12
2.4轴承和轴承座的类型……………………………………………………………15
2.4.1轴承的类型……………………………………………………………………15
2.4.2轴承座的类型…………………………………………………………………15
2.5其它主要零件的选择……………………………………………………………15
2.5.1停车梁的选择…………………………………………………………………15
2.5.2支承梁与活动梁的选择………………………………………………………15
2.6本章小结…………………………………………………………………………17
摘要……………………………………………………………………………………1
关键词…………………………………………………………………………………1
1前言…………………………………………………………………………………2
1.1课题背景…………………………………………………………………………2
1.2 国外研究现状 ……………………………………………………………………3
1.3 国内研究现状……………………………………………………………………4
1.4 主要研究内容……………………………………………………………………4
2 方案选择及结构设计……………………………………………………………… 5
2.1立体车库总体结构设计…………………………………………………………5
2.1.1车型及车库参数………………………………………………………………5
2.1.2 车库工作流程…………………………………………………………………5
2.2 液压系统部件的选择与计算……………………………………………………5
2.2.1液压缸的选择与计算…………………………………………………………5
2.2.2液压泵的选择…………………………………………………………………8
2.2.3泵电动机的选择………………………………………………………………9
2.3传动部件的选择与计算…………………………………………………………10
2.3.1减速机的选择…………………………………………………………………10
2.3.2链条的设计……………………………………………………………………10
2.3.3链轮的设计……………………………………………………………………12
2.4轴承和轴承座的类型……………………………………………………………15
2.4.1轴承的类型……………………………………………………………………15
2.4.2轴承座的类型…………………………………………………………………15
2.5其它主要零件的选择……………………………………………………………15
2.5.1停车梁的选择…………………………………………………………………15
2.5.2支承梁与活动梁的选择………………………………………………………15
2.6本章小结…………………………………………………………………………17
3 主要部件强度刚度校核……………………………………………………………17
3.1.1主动轴的强度校核……………………………………………………………17
3.1.2主动轴的刚度校核……………………………………………………………19
3.1.3从动轴的强度校核……………………………………………………………21
3.1.4从动轴的刚度校核……………………………………………………………25
3.2轴承和键的校核…………………………………………………………………27
3.2.1轴承的校核……………………………………………………………………27
3.2.2键的强度校核…………………………………………………………………28
3.3梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………………29
3.3.1梁的自由扭转计算……………………………………………………………29
3.3.2活动梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………30
3.3.3停车梁的强度和刚度校核……………………………………………………36
3.4本章小结…………………………………………………………………………40
结束语…………………………………………………………………………………40
参考文献………………………………………………………………………………40
致谢 ……………………………………………………………………………………41