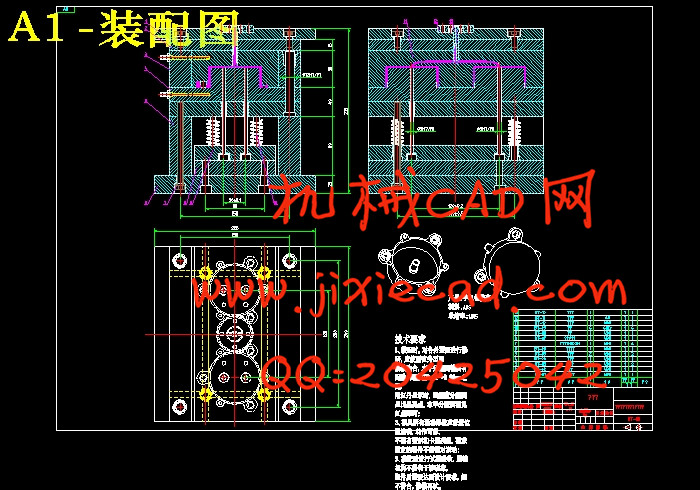
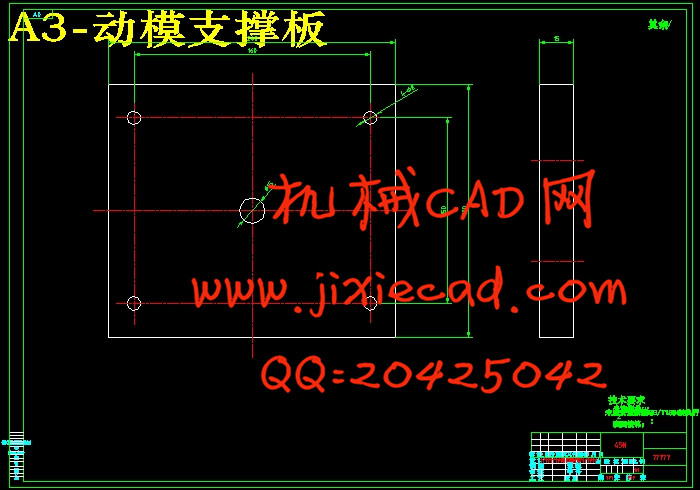
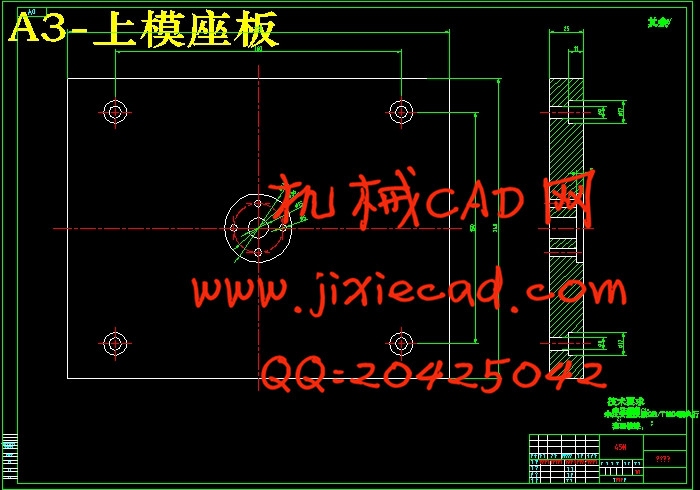
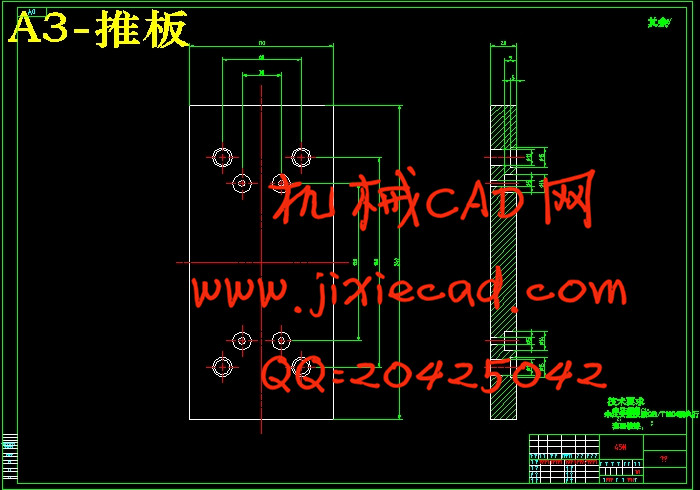
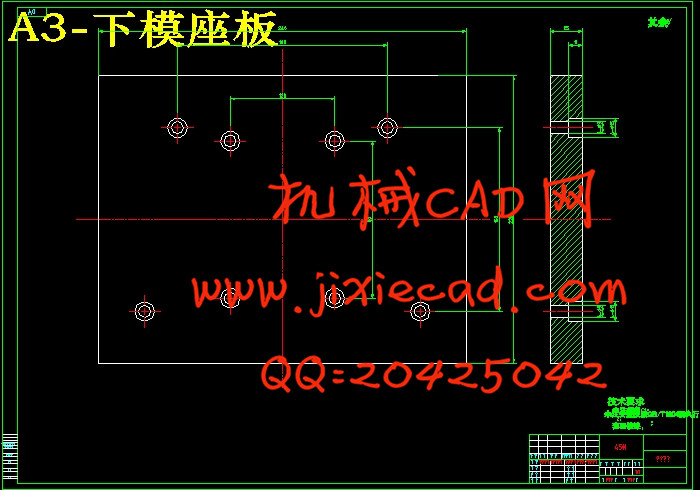
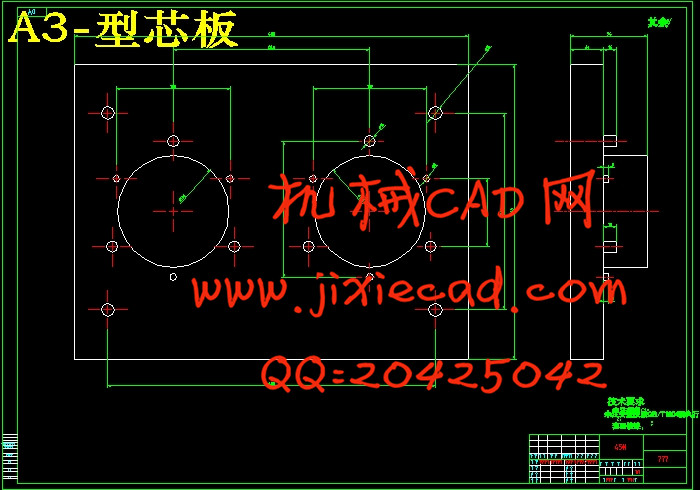
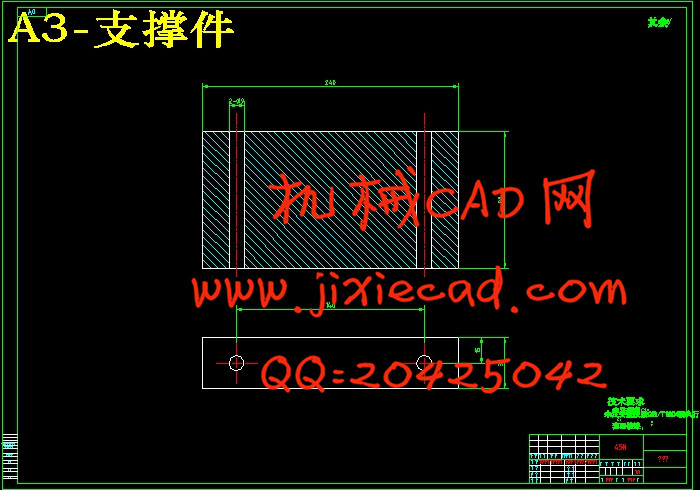
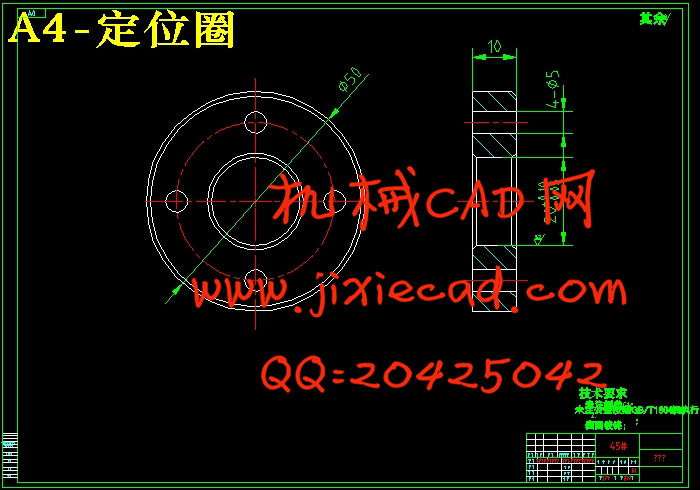
设计简介
摘要
根据塑料制品的要求,了解塑件的用途,分析塑件的工艺性、尺寸精度等技术要求,考量塑件制件尺寸。本模具采用一模二腔,直浇口进料,注射机采用HTF80XB 型号,设置冷却系统,CAD和UG绘制二维总装图和零件图,选择模具合理的加工方法。附上说明书,系统地运用简要的文字,简明的示意图和和计算等分析塑件,从而作出合理的模具设计。关键词:塑料制品;模具设计;CAD绘制二维图;塑件。
Abstract
To understand the use of plastic parts in accordance with the requirements of the plastic products, analysis of the technical requirements of the plastic parts of the process, dimensional accuracy, select the workpiece size of the plastic parts. The mold using a sprue gate feed injection machine adopts TOSHIBA the EC40-Y models, and set a cooling system, CAD and UG drawing two-dimensional assembly diagram and parts diagram, reasonable mold processing methods. Attach a manual, use brief text, a concise diagram and calculated analysis of plastic parts, in order to make a reasonable mold design.
Keywords: mechanical design; mold design; CAD drawing two-dimensional map; molde
To understand the use of plastic parts in accordance with the requirements of the plastic products, analysis of the technical requirements of the plastic parts of the process, dimensional accuracy, select the workpiece size of the plastic parts. The mold using a sprue gate feed injection machine adopts TOSHIBA the EC40-Y models, and set a cooling system, CAD and UG drawing two-dimensional assembly diagram and parts diagram, reasonable mold processing methods. Attach a manual, use brief text, a concise diagram and calculated analysis of plastic parts, in order to make a reasonable mold design.
Keywords: mechanical design; mold design; CAD drawing two-dimensional map; molde
目 录
第1章 绪论 1
1.1 塑料简介 1
1.2 注塑成型及注塑模 2
第2章 塑料材料分析 3
2.1 塑料材料的基本特性 4
第3章 塑件的工艺分析 6
3.1 塑件的结构设计 7
3.2 塑件尺寸及精度 8
第4章 注射成型工艺方案及模具结构的分析确定 9
4.1 浇口种类的确定 9
4.2 型腔数目的确定 10
4.3 注射机的选择和校核 10
4.3.1注射量的校核 11
4.3.2塑件在分型面上的投影面积与锁模力的校核 12
4.3.3模具与注射机安装模具部分相关尺寸校核 12
第5章 注射模具结构设计 12
5.1 分型面的设计 12
5.2 型腔的布局 12
5.3 浇注系统的设计 13
5.3.1浇注系统组成 13
5.3.2主流道的设计 14
5.3.3分流道的设计 14
5.3.4浇口的设计 15
5.3.5冷料穴的设计 15
5.4注射模成型零部件的设计[7] 16
5.4.1成型零部件结构设计 17
5.4.2成型零部件工作尺寸的计算 17
5.5排气结构设计 17
5.5.1 凹模宽度尺寸的计算 17
5.5.2 凹模长度尺寸的计算 18
5.5.3 凹模高度尺寸的计算 18
5.5.4 凸模宽度尺寸的计算 19
5.5.5 凸模长度的计算 20
5.5.6凸模高度尺寸的计算 21
5.6脱模机构的设计 21第1章 绪论 1
1.1 塑料简介 1
1.2 注塑成型及注塑模 2
第2章 塑料材料分析 3
2.1 塑料材料的基本特性 4
第3章 塑件的工艺分析 6
3.1 塑件的结构设计 7
3.2 塑件尺寸及精度 8
第4章 注射成型工艺方案及模具结构的分析确定 9
4.1 浇口种类的确定 9
4.2 型腔数目的确定 10
4.3 注射机的选择和校核 10
4.3.1注射量的校核 11
4.3.2塑件在分型面上的投影面积与锁模力的校核 12
4.3.3模具与注射机安装模具部分相关尺寸校核 12
第5章 注射模具结构设计 12
5.1 分型面的设计 12
5.2 型腔的布局 12
5.3 浇注系统的设计 13
5.3.1浇注系统组成 13
5.3.2主流道的设计 14
5.3.3分流道的设计 14
5.3.4浇口的设计 15
5.3.5冷料穴的设计 15
5.4注射模成型零部件的设计[7] 16
5.4.1成型零部件结构设计 17
5.4.2成型零部件工作尺寸的计算 17
5.5排气结构设计 17
5.5.1 凹模宽度尺寸的计算 17
5.5.2 凹模长度尺寸的计算 18
5.5.3 凹模高度尺寸的计算 18
5.5.4 凸模宽度尺寸的计算 19
5.5.5 凸模长度的计算 20
5.5.6凸模高度尺寸的计算 21
5.6.1脱模机构的选用原则 22
5.6.2脱模力 23
5.6.3推板机构具体设计 24
5.7直向抽芯机构类型选择 25
5.7.1滑块直抽芯机构设计 26
总结 27
致谢 28
参考文献 29